RNA uridylation and decay in plants
- PMID: 30397100
- PMCID: PMC6232585
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0163
RNA uridylation and decay in plants
Abstract
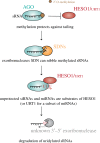
RNA uridylation consists of the untemplated addition of uridines at the 3' extremity of an RNA molecule. RNA uridylation is catalysed by terminal uridylyltransferases (TUTases), which form a subgroup of the terminal nucleotidyltransferase family, to which poly(A) polymerases also belong. The key role of RNA uridylation is to regulate RNA degradation in a variety of eukaryotes, including fission yeast, plants and animals. In plants, RNA uridylation has been mostly studied in two model species, the green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana Plant TUTases target a variety of RNA substrates, differing in size and function. These RNA substrates include microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering silencing RNAs (siRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and mRNA fragments generated during post-transcriptional gene silencing. Viral RNAs can also get uridylated during plant infection. We describe here the evolutionary history of plant TUTases and we summarize the diverse molecular functions of uridylation during RNA degradation processes in plants. We also outline key points of future research.This article is part of the theme issue '5' and 3' modifications controlling RNA degradation'.
Keywords: RNA decay; RNA degradation; mRNAs; terminal nucleotidyltransferase; uridylation.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
