Step Sizes and Rate Constants of Single-headed Cytoplasmic Dynein Measured with Optical Tweezers
- PMID: 30397249
- PMCID: PMC6218510
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34549-7
Step Sizes and Rate Constants of Single-headed Cytoplasmic Dynein Measured with Optical Tweezers
Abstract
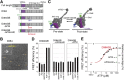
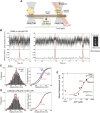
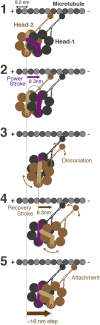
A power stroke of dynein is thought to be responsible for the stepping of dimeric dynein. However, the actual size of the displacement driven by a power stroke has not been directly measured. Here, the displacements of single-headed cytoplasmic dynein were measured by optical tweezers. The mean displacement of dynein interacting with microtubule was ~8 nm at 100 µM ATP, and decreased sigmoidally with a decrease in the ATP concentration. The ATP dependence of the mean displacement was explained by a model that some dynein molecules bind to microtubule in pre-stroke conformation and generate 8-nm displacement, while others bind in the post-stroke one and detach without producing a power stroke. Biochemical assays showed that the binding affinity of the post-stroke dynein to a microtubule was ~5 times higher than that of pre-stroke dynein, and the dissociation rate was ~4 times lower. Taking account of these rates, we conclude that the displacement driven by a power stroke is 8.3 nm. A working model of dimeric dynein driven by the 8-nm power stroke was proposed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

