Comparative genomics of the major parasitic worms
- PMID: 30397333
- PMCID: PMC6349046
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0262-1
Comparative genomics of the major parasitic worms
Abstract
Parasitic nematodes (roundworms) and platyhelminths (flatworms) cause debilitating chronic infections of humans and animals, decimate crop production and are a major impediment to socioeconomic development. Here we report a broad comparative study of 81 genomes of parasitic and non-parasitic worms. We have identified gene family births and hundreds of expanded gene families at key nodes in the phylogeny that are relevant to parasitism. Examples include gene families that modulate host immune responses, enable parasite migration though host tissues or allow the parasite to feed. We reveal extensive lineage-specific differences in core metabolism and protein families historically targeted for drug development. From an in silico screen, we have identified and prioritized new potential drug targets and compounds for testing. This comparative genomics resource provides a much-needed boost for the research community to understand and combat parasitic worms.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

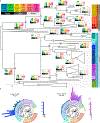



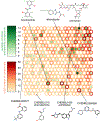
Comment in
-
Opening up a large can of worms.Nat Genet. 2019 Jan;51(1):10-11. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0317-3. Nat Genet. 2019. PMID: 30514910 No abstract available.
References
-
- G.B.D. 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388, 1545–1602 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Charlier J, van der Voort M, Kenyon F, Skuce P & Vercruysse J Chasing helminths and their economic impact on farmed ruminants. Trends Parasitol 30, 361–7 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Furtado LF, de Paiva Bello AC & Rabelo EM Benzimidazole resistance in helminths: From problem to diagnosis. Acta Trop 162, 95–102 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Kaplan RM & Vidyashankar AN An inconvenient truth: global worming and anthelmintic resistance. Vet Parasitol 186, 70–8 (2012). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Gremme G, Steinbiss S & Kurtz S GenomeTools: a comprehensive software library for efficient processing of structured genome annotations. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 10, 645–56 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Boetzer M, Henkel CV, Jansen HJ, Butler D & Pirovano W Scaffolding pre-assembled contigs using SSPACE. Bioinformatics 27, 578–9 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MC_PC_18048/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- REI18431/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S000453/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L001020/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R56 AI081803/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI126466/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI081803/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM097435/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 AI125473/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K01207X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

