Gut microbiota and intestinal FXR mediate the clinical benefits of metformin
- PMID: 30397356
- PMCID: PMC6479226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0222-4
Gut microbiota and intestinal FXR mediate the clinical benefits of metformin
Abstract
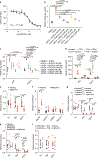
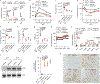
The anti-hyperglycemic effect of metformin is believed to be caused by its direct action on signaling processes in hepatocytes, leading to lower hepatic gluconeogenesis. Recently, metformin was reported to alter the gut microbiota community in humans, suggesting that the hyperglycemia-lowering action of the drug could be the result of modulating the population of gut microbiota. However, the critical microbial signaling metabolites and the host targets associated with the metabolic benefits of metformin remained elusive. Here, we performed metagenomic and metabolomic analysis of samples from individuals with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (T2D) naively treated with metformin for 3 d, which revealed that Bacteroides fragilis was decreased and the bile acid glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA) was increased in the gut. These changes were accompanied by inhibition of intestinal farnesoid X receptor (FXR) signaling. We further found that high-fat-diet (HFD)-fed mice colonized with B. fragilis were predisposed to more severe glucose intolerance, and the metabolic benefits of metformin treatment on glucose intolerance were abrogated. GUDCA was further identified as an intestinal FXR antagonist that improved various metabolic endpoints in mice with established obesity. Thus, we conclude that metformin acts in part through a B. fragilis-GUDCA-intestinal FXR axis to improve metabolic dysfunction, including hyperglycemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Effects of metformin mediated by gut microbiota.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018 Dec;15(1):2. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0133-y. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30429579 No abstract available.
-
A Gut Feeling for Metformin.Cell Metab. 2018 Dec 4;28(6):808-810. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.11.012. Cell Metab. 2018. PMID: 30517894
-
Metformin action through the microbiome and bile acids.Nat Med. 2018 Dec;24(12):1789-1790. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0273-6. Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 30523325 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

