B Cell Regulation in Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 30397522
- PMCID: PMC6209408
B Cell Regulation in Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
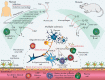
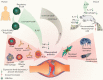
Antibody-independent B cell effector functions play an important role in the development and suppression of the immune response. An extensive body of data on cytokine regulation of the immune response by B lymphocytes has been accumulated over the past fifteen years. In this review, we focused on the mechanisms of inflammatory response suppression by subpopulations of regulatory B cells in health and autoimmune pathologies.
Keywords: Breg, regulatory B cells; CD19+CD24(hi)CD38(hi); IL-10; IL-35; Multiple sclerosis; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures


References
-
- Katz S.I., Parker D., Turk J.L.. Nature. 1974;251(5475):550–551. - PubMed
-
- Flores-Borja F., Bosma A., Ng D., Reddy V., Ehrenstein M.R., Isenberg D.A., Mauri C., Sci. Transl. Med. 2013;5(173):173ra123. - PubMed
-
- Fillatreau S., Sweenie C.H., McGeachy M.J., Gray D., Anderton S.M.. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3(10):944–950. - PubMed
-
- Couper K.N., Blount D.G., Riley E.M.. J. Immunol. 2008;180(9):5771–5777. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
