Effect of PEGylation on assembly morphology and cellular uptake of poly ethyleneimine-cholesterol conjugates for delivery of sorafenib tosylate in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 30397579
- PMCID: PMC6209830
- DOI: 10.15171/bi.2018.27
Effect of PEGylation on assembly morphology and cellular uptake of poly ethyleneimine-cholesterol conjugates for delivery of sorafenib tosylate in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
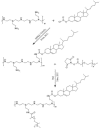
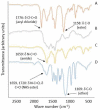
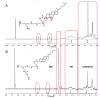
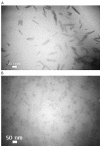
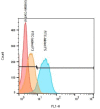
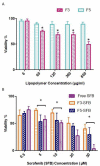
Introduction: Sorafenib (SFB) is an FDA-approved chemotherapeutic agent with a high partition coefficient (log P = 4.34) for monotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The oral bioavailability is low and variable, so it was aimed to study the application of the polymeric nanoassembly of cholesterol conjugates of branched polyethyleneimine (PEI) for micellar solubilization of SFB and to investigate the impact of the polymer PEGylation on the physicochemical and cellular characteristics of the lipopolymeric dispersions. Methods: Successful synthesis of cholesterol-PEI lipopolymers, either native or PEGylated, was confirmed by FTIR, 1H-NMR, pyrene assay methods. The nanoassemblies were also characterized in terms of morphology, particle size distribution and zeta-potential by TEM and dynamic light scattering (DLS). The SFB loading was optimized using general factorial design. Finally, the effect of particle characteristics on cellular uptake and specific cytotoxicity was investigated by flow cytometry and MTT assay in HepG2 cells. Results: Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showed that PEGylation of the lipopolymers reduces the size and changes the morphology of the nanoassembly from rod-like to spherical shape. However, PEGylation of the lipopolymer increased critical micelle concentration (CMC) and reduced the drug loading. Moreover, the particle shape changes from large rods to small spheres promoted the cellular uptake and SFB-related cytotoxicity. Conclusion: The combinatory effects of enhanced cellular uptake and reduced general cytotoxicity can present PEGylated PEI-cholesterol conjugates as a potential carrier for delivery of poorly soluble chemotherapeutic agents such as SFB in HCC that certainly requires further investigations in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Lipopolymer; PEGylation; Poly ethyleneimine; Polymeric micelles; Sorafenib tosylate.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources