Three Severe Cases of Viral Infections with Post-Kidney Transplantation Successfully Confirmed by Polymerase Chain Reaction and Flow Cytometry
- PMID: 30397600
- PMCID: PMC6206958
- DOI: 10.1159/000493092
Three Severe Cases of Viral Infections with Post-Kidney Transplantation Successfully Confirmed by Polymerase Chain Reaction and Flow Cytometry
Abstract
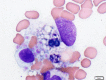
Viral infections in patients with post-kidney transplantation are often difficult to diagnose as well as treat. We herein report three cases with severe viral infections after kidney transplantation. All their causative pathogens could be detected promptly by polymerase chain reaction and flow cytometry during the early stages of infection. These examinations would also be of great use to monitor therapeutic responses and disease activity. It is indeed true that no specific treatment is available for most of the viral infections, but we should be aware that some infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus infection, can be treatable with prompt and specific treatment, such as rituximab.
Keywords: Flow cytometry; Kidney transplantation; Polymerase chain reaction; Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease; Rituximab; Viral infection.
Figures

References
-
- Jensik SC. Tacrolimus (FK 506) in kidney transplantation: three-year survival results of the US multicenter, randomized, comparative trial. FK 506 Kidney Transplant Study Group. Transplant Proc. 1998 Jun;30((4)):1216–8. - PubMed
-
- Sollinger HW, Deierhoi MH, Belzer FO, Diethelm AG, Kauffman RS. RS-61443—a phase I clinical trial and pilot rescue study. Transplantation. 1992 Feb;53((2)):428–32. - PubMed
-
- Nashan B, Moore R, Amlot P, Schmidt AG, Abeywickrama K, Soulillou JP. Randomised trial of basiliximab versus placebo for control of acute cellular rejection in renal allograft recipients. CHIB 201 International Study Group. Lancet. 1997 Oct;350((9086)):1193–8. - PubMed
-
- Tydén G, Kumlien G, Genberg H, Sandberg J, Lundgren T, Fehrman I. ABO incompatible kidney transplantations without splenectomy, using antigen-specific immunoadsorption and rituximab. Am J Transplant. 2005 Jan;5((1)):145–8. - PubMed
-
- Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007 Feb;48((2)):124–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

