Identification and characterization of GH11 xylanase and GH43 xylosidase from the chytridiomycetous fungus, Rhizophlyctis rosea
- PMID: 30397764
- PMCID: PMC6373445
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-018-9431-5
Identification and characterization of GH11 xylanase and GH43 xylosidase from the chytridiomycetous fungus, Rhizophlyctis rosea
Abstract
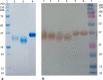
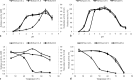
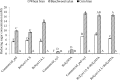
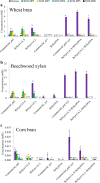
The early-lineage, aerobic, zoosporic fungi from the Chytridiomycota constitute less than 1% of the described fungi and can use diverse sources of nutrition from plant or animal products. One of the ancestral sources of fungal nutrition could be products following enzymatic degradation of plant material. However, carbohydrate-active enzymes from these ancient fungi have been less studied. A GH11 xylanase (RrXyn11A) (EC 3.2.1.8) and a GH43 xylosidase (RrXyl43A) (EC 3.2.1.37) were identified from an early-lineage aerobic zoosporic fungus, Rhizophlyctis rosea NBRC 105426. Both genes were heterologously expressed in Pichia pastoris and the recombinant enzymes were purified and characterized. The optimal pH for recombinant RrXyn11A and RrXyl43A was pH 7. RrXyn11A had high stability over a wide range of pH (4-8) and temperature (25-70 °C). RrXyn11A also showed high substrate specificity on both azurine-cross-linked (AZCL) arabinoxylan and AZCL xylan. RrXyl43A had β-xylosidase and minor α-L-arabinofuranosidase activity. This enzyme showed low product inhibition and retained 51% activity in the presence of 100 mM xylose. A combination of RrXyn11A and RrXyl43A exhibited significantly higher hydrolytic and polymer degradation capability and xylose release on wheat bran and beechwood xylan compared to treatment with commercial enzymes. This study was the first to heterologously express and characterize the GH11 xylanase (RrXyn11A) and GH43 xylosidase (RrXyl43A) from the ancient fungus, R. rosea. Meanwhile, this study also demonstrated that the enzymes from the ancient fungus R. rosea can be easily handled and heterologously expressed in Pichia, which presents a promising path to a new source of enzymes for biomass degradation.
Keywords: Chytridiomycota; GH11 xylanase; GH43 xylosidase; HotPep; Rhizophlyctis rosea.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two xylose-tolerant GH43 bifunctional β-xylosidase/α-arabinosidases and one GH11 xylanase from Humicola insolens and their synergy in the degradation of xylan.Food Chem. 2014 Apr 1;148:381-7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.062. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24262572
-
Characterization of the arabinoxylan-degrading machinery of the thermophilic bacterium Herbinix hemicellulosilytica-Six new xylanases, three arabinofuranosidases and one xylosidase.J Biotechnol. 2017 Sep 10;257:122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.04.023. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28450260
-
Biochemical characterization of a novel GH43 family β-xylosidase from Bacillus pumilus.Food Chem. 2019 Oct 15;295:653-661. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.163. Epub 2019 May 24. Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 31174809
-
Heterologous expression in Pichia pastoris and characterization of a novel GH11 xylanase from saline-alkali soil with excellent tolerance to high pH, high salt concentrations and ethanol.Protein Expr Purif. 2017 Nov;139:71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Protein Expr Purif. 2017. PMID: 28602686 Review.
-
Xylanases: from biology to biotechnology.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1996;13:101-31. doi: 10.1080/02648725.1996.10647925. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1996. PMID: 8948110 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Agroforestry Practices on Soil Microbial Diversity and Nutrient Cycling in Atlantic Rainforest Cocoa Systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 22;25(21):11345. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111345. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518901 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the Alteration in Rumen Microbiome and Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes Profile with Forage of Muskoxen Rumen through Comparative Metatranscriptomics.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 30;10(1):71. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010071. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 35056520 Free PMC article.
-
High-level production of xylose from agricultural wastes using GH11 endo-xylanase and GH43 β-xylosidase from Bacillus sp.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2022 Oct;45(10):1705-1717. doi: 10.1007/s00449-022-02778-w. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2022. PMID: 36063213
-
Enzymes of early-diverging, zoosporic fungi.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Sep;103(17):6885-6902. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09983-w. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31309267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving the Catalytic Properties of Xylanase from Alteromones Macleadii H35 Through Sequence Analysis.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;196(11):7736-7746. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-04936-0. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38538873
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

