Aquaporins in the lung
- PMID: 30397774
- PMCID: PMC6435619
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-018-2232-y
Aquaporins in the lung
Abstract
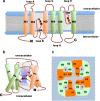
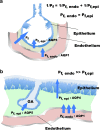
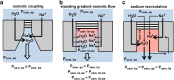
The lung is the interface between air and blood where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs. The surface liquid that is directly exposed to the gaseous compartment covers both conducting airways and respiratory zone and forms the air-liquid interface. The barrier that separates this lining fluid of the airways and alveoli from the extracellular compartment is the pulmonary epithelium. The volume of the lining fluid must be kept in a range that guarantees an appropriate gas exchange and other functions, such as mucociliary clearance. It is generally accepted that this is maintained by balancing resorptive and secretory fluid transport across the pulmonary epithelium. Whereas osmosis is considered as the exclusive principle of fluid transport in the airways, filtration may contribute to alveolar fluid accumulation under pathologic conditions. Aquaporins (AQP) facilitate water flux across cell membranes, and as such, they provide a transcellular route for water transport across epithelia. However, their contribution to near-isosmolar fluid conditions in the lung still remains elusive. Herein, we discuss the role of AQPs in the lung with regard to fluid homeostasis across the respiratory epithelium.
Keywords: Aquaporin; Endothelium; Epithelium; Lung; Water transport.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lung edema clearance: 20 years of progress: invited review: role of aquaporin water channels in fluid transport in lung and airways.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002 Dec;93(6):2199-206. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01171.2001. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002. PMID: 12433939 Review.
-
Role of aquaporins in lung liquid physiology.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2007 Dec 15;159(3):324-30. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2007.02.012. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17369110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of aquaporins in alveolar fluid clearance in neonatal and adult lung, and in oedema formation following acute lung injury: studies in transgenic aquaporin null mice.J Physiol. 2000 Jun 15;525 Pt 3(Pt 3):771-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00771.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10856128 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and localization of epithelial aquaporins in the adult human lung.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001 Mar;24(3):224-34. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.24.3.4367. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11245621
-
Salt and water transport across alveolar and distal airway epithelia in the adult lung.Am J Physiol. 1996 Apr;270(4 Pt 1):L487-503. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1996.270.4.L487. Am J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8928808 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma TNFRSF11B as a New Predictive Inflammatory Marker of Sepsis-ARDS with Endothelial Dysfunction.J Proteome Res. 2023 Nov 3;22(11):3640-3651. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00576. Epub 2023 Oct 18. J Proteome Res. 2023. PMID: 37851947 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Mechanisms and Pharmacological Modulators Governing Diverse Aquaporin Functions in Human Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 26;23(3):1388. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031388. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Cooperation between Aquaporin 5 and TRPV4.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 1;23(19):11634. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911634. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection of human-induced pluripotent stem cells-derived lung lineage cells evokes inflammatory and chemosensory responses by targeting mitochondrial pathways.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Jul;237(7):2913-2928. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30755. Epub 2022 Apr 23. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35460571 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Transplant Recipients Show Limited Lung Diffusion Capacity but Similar Hydrogen Peroxide Exhalation as Healthy Matched Volunteers: A Pilot Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 7;12(22):6964. doi: 10.3390/jcm12226964. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrami L, Tacnet F, Ripoche P. Evidence for a glycerol pathway through aquaporin 1 (CHIP28) channels. Pflugers Arch. 1995;430:447–458. - PubMed
-
- Abrami L, Berthonaud V, Rousselet G, Tacnet F, Ripoche P, Deen PMT. Glycerol permeability of mutant aquaporin 1 and other AQP-MIP proteins: inhibition studies. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol. 1996;431:408–414. - PubMed
-
- Agre P, Sasaki S, Chrispeels MJ. Aquaporins: a family of water channel proteins. Am J Phys. 1993;265:F461. - PubMed
-
- Alleva K, Niemietz CM, Sutka M, Maurel C, Parisi M, Tyerman SD, Amodeo G. Plasma membrane of beta vulgaris storage root shows high water channel activity regulated by cytoplasmic pH and a dual range of calcium concentrations. J Exp Bot. 2006;57:609–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

