Structure-activity relationships of bath salt components: substituted cathinones and benzofurans at biogenic amine transporters
- PMID: 30397775
- PMCID: PMC6500773
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-018-5059-5
Structure-activity relationships of bath salt components: substituted cathinones and benzofurans at biogenic amine transporters
Abstract
Rationale: New psychoactive substances (NPSs), including substituted cathinones and other stimulants, are synthesized, sold on the Internet, and ingested without knowledge of their pharmacological activity and/or toxicity. In vitro pharmacology plays a role in therapeutic drug development, drug-protein in silico interaction modeling, and drug scheduling.
Objectives: The goal of this research was to determine mechanisms of action that may indicate NPS abuse liability.
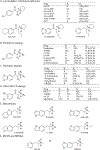
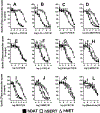
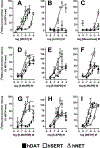
Methods: Affinities to displace the radioligand [125I]RTI-55 and potencies to inhibit [3H]neurotransmitter uptake for 22 cathinones, 6 benzofurans and another stimulant were characterized using human embryonic kidney cells stably expressing recombinant human transporters for dopamine, norepinephrine, or serotonin (hDAT, hNET, or hSERT, respectively). Selected compounds were tested for potencies and efficacies at inducing [3H]neurotransmitter release via the transporters. Computational modeling was conducted to explain plausible molecular interactions established by NPS and transporters.
Results: Most α-pyrrolidinophenones had high hDAT potencies and selectivities in uptake assays, with hDAT/hSERT uptake selectivity ratios of 83-360. Other substituted cathinones varied in their potencies and selectivities, with N-ethyl-hexedrone and N-ethyl-pentylone having highest hDAT potencies and N-propyl-pentedrone having highest hDAT selectivity. 4-Cl-ethcathinone and 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-propylcathinone had higher hSERT selectivity. Benzofurans generally had low hDAT selectivity, especially 1-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-N-methylpropan-2-amine, with 25-fold higher hSERT potency. Consistent with this selectivity, the benzofurans were releasers at hSERT. Modeling indicated key amino acids in the transporters' binding pockets that influence drug affinities.
Conclusions: The α-pyrrolidinophenones, with high hDAT selectivity, have high abuse potential. Lower hDAT selectivity among benzofurans suggests similarity to methylenedioxymethamphetamine, entactogens with lower stimulant activity.
Keywords: Benzofurans; Cathinones; New psychoactive substances; Pharmacology; Psychostimulant; Transporter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure-Activity Relationships of Substituted Cathinones, with Transporter Binding, Uptake, and Release.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017 Jan;360(1):33-47. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.236349. Epub 2016 Oct 31. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017. PMID: 27799294 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of drug interactions with recombinant biogenic amine transporters expressed in the same cell type.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 May;289(2):877-85. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10215666
-
α-PPP and its derivatives are selective partial releasers at the human norepinephrine transporter: A pharmacological characterization of interactions between pyrrolidinopropiophenones and high and low affinity monoamine transporters.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Jun 1;190:108570. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108570. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33864800
-
Human genetics and pharmacology of neurotransmitter transporters.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;(175):327-71. doi: 10.1007/3-540-29784-7_16. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16722243 Review.
-
Using Ca2+-channel biosensors to profile amphetamines and cathinones at monoamine transporters: electro-engineering cells to detect potential new psychoactive substances.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Mar;236(3):973-988. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5103-5. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30448989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relative reinforcing effects of dibutylone, ethylone, and N-ethylpentylone: self-administration and behavioral economics analysis in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Sep;239(9):2875-2884. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06173-x. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35716192
-
Molecular mechanisms of action of stimulant novel psychoactive substances that target the high-affinity transporter for dopamine.Neuronal Signal. 2021 Nov 17;5(4):NS20210006. doi: 10.1042/NS20210006. eCollection 2021 Dec. Neuronal Signal. 2021. PMID: 34888062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induced fit, ensemble binding space docking and Monte Carlo simulations of MDMA 'ecstasy' and 3D pharmacophore design of MDMA derivatives on the human serotonin transporter (hSERT).Heliyon. 2021 Aug 13;7(8):e07784. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07784. eCollection 2021 Aug. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34458620 Free PMC article.
-
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine-like discriminative stimulus effects of pyrrolidinyl cathinones in rats.J Psychopharmacol. 2020 Jul;34(7):778-785. doi: 10.1177/0269881120914213. Epub 2020 Jun 13. J Psychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32536334 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaco-Toxicological Effects of Atypical Synthetic Cathinone Mephtetramine (MTTA) in Mice: Possible Reasons for Its Brief Appearance over NPSs Scene.Brain Sci. 2023 Jan 18;13(2):161. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13020161. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 36831704 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

