Epidemiological investigations of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in selected districts of Borana zone, Southern Oromia, Ethiopia
- PMID: 30397847
- PMCID: PMC6513795
- DOI: 10.1007/s11250-018-1744-y
Epidemiological investigations of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in selected districts of Borana zone, Southern Oromia, Ethiopia
Abstract
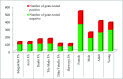
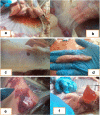
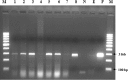
From November 2016 to April 2017, a cross-sectional study to determine the sero-prevalence of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP) and to investigate its epidemiology was conducted in selected districts of Borana zone in Ethiopia. In addition, the study aimed at identifying Mccp antigens using species specific primer of PCR. A multistage random sampling was implemented to select districts, pastoral associations (villages), and households. A total of 890 serum samples of small ruminants that had not been vaccinated (goats n = 789 and sheep n = 101) were collected and screened for the presence of antibodies against Mycoplasma capricolum subspecies capripneumoniae using a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Lung tissues and pleural fluid samples were collected from 3 sero-positive and clinically suspected goats for isolation of Mycoplasma capricolum subspecies capripneumoniae. Serology showed that overall 31.2% (246/789) of goats and 12.9% (13/101) of sheep were positive with statistically significant differences between districts (p = 0.001). Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that goats from Moyale and Yabello districts had higher odds of being positive than goats from Elwoya district with odd ratios of 2.05 and 1.61, respectively. Age of goats was also significantly associated with sero-positivity (OR = 1.47; CI 95% 1.2-1.8). Mycoplasma capricolum subspecies capripneumoniae was identified in 6 (75%) of the tissue samples using species-specific primer of PCR. Besides improving the understanding of the epidemiology of CCPP in the selected districts and demonstrating its wide distribution, the study highly also provides evidence of the possible role of sheep in the maintenance of the disease.
Keywords: CCPP; Risk factors; Sero-prevalence; cELISA.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethical considerations
“Ethical clearance on the use of sheep and goats for this study was obtained from animal research ethics review committee of Addis Ababa University, College of Veterinary Medicine and Agriculture, before the start of this study. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.” The owners of sheep and goats used in this study and the local administration were informed about the study and the owners revealed their consent in the presence of administrative bodies.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Seroprevalence and associated risk factors of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in selected districts of South Wollo Zone Northeast Ethiopia.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Jul 16;20(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04181-x. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39014419 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in Kefta Humera, Alamata (Tigray) and Aba-'ala (Afar), Northern Ethiopia.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2009 Jun;41(5):803-6. doi: 10.1007/s11250-008-9255-x. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2009. PMID: 18989743
-
Sero-prevalence and associated risk factors of peste des petits ruminants and contagious caprine pleuro-pneumonia in goats and sheep in the Southern Zone of Tanzania.Prev Vet Med. 2014 Sep 1;116(1-2):138-44. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2014.06.013. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Prev Vet Med. 2014. PMID: 25022914
-
Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia - a comprehensive review.Vet Q. 2019 Dec;39(1):1-25. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2019.1580826. Vet Q. 2019. PMID: 30929577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP) in Ethiopia.Acta Trop. 2016 Jun;158:231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.02.023. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Acta Trop. 2016. PMID: 26943994
Cited by
-
Seroprevalence and associated risk factors of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in selected districts of South Wollo Zone Northeast Ethiopia.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Jul 16;20(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04181-x. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39014419 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Candidates for Vaccine Development Against Mycoplasma Capricolum Subspecies Capripneumoniae (Mccp)-Current Knowledge and Future Prospects.Vaccines (Basel). 2019 Jul 23;7(3):71. doi: 10.3390/vaccines7030071. Vaccines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31340571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial distribution and clustering of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in goats of Amhara region, Ethiopia.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 21;10(19):e38180. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38180. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39386806 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in acid-base balance, blood gases, and hematobiochemical profiles of whole-blood and thoracic fluid in goats with contagious caprine pleuropneumonia.Vet World. 2021 Jul;14(7):1874-1878. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2021.1874-1878. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Vet World. 2021. PMID: 34475711 Free PMC article.
-
Co-occurrence of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia and pasteurellosis in goats of sub-Saharan region: systematic review.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024 Sep 30;56(8):303. doi: 10.1007/s11250-024-04160-2. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024. PMID: 39347878
References
-
- Aklilu F, Asfaw Y, Baumann M, Abie G. Epidemiological study of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP) in selected districts of Gambella Region, Western Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2015;10(24):2470–2479. doi: 10.5897/AJAR2014.9264. - DOI
-
- Atim S, Ayebazibwe C, Mwiine F, Erume J, Tweyongyere R. A Survey for contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in Agago and Otuke districts in Northern Uganda. Open J Vet Med. 2016;6(1):9–14. doi: 10.4236/ojvm.2016.61002. - DOI
-
- AU-IBAR, 2015. Standard methods and procedures (SMPs): for contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP) in the Greater Horn of Africa, Nairobi
-
- Bekele, T., Asfaw, Y., GebreEgziabeher, B. and Getachew Abebe, G. 2011. Sero-prevalence of contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in Borana and Guji lowlands, Southern Ethiopia. Ethiop. Vet. J. 15(2): 69–76.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

