Clinical Utility of Reinterpreting Previously Reported Genomic Epilepsy Test Results for Pediatric Patients
- PMID: 30398534
- PMCID: PMC6583457
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.2302
Clinical Utility of Reinterpreting Previously Reported Genomic Epilepsy Test Results for Pediatric Patients
Abstract
Importance: Clinical genomic tests that examine the DNA sequence of large numbers of genes are commonly used in the diagnosis and management of epilepsy in pediatric patients. The permanence of genomic test result interpretations is not known.
Objective: To investigate the value of reinterpreting previously reported genomic test results.
Design, setting, and participants: This study retrospectively reviewed and reinterpreted genomic test results from July 1, 2012, to August 31, 2015, for pediatric patients who previously underwent genomic epilepsy testing at a single tertiary care pediatric health care facility. Reinterpretation of previously reported variants was conducted in May 2017.
Main outcomes and measures: Patient reports from clinical genomic epilepsy tests were reviewed, and all reported genetic variants were reinterpreted using 2015 consensus standards and guidelines for interpreting hereditary genetic variants. Three classification tiers were used in the reinterpretation: pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant, variant of uncertain significance (VUS), or benign or likely benign variant.
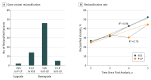
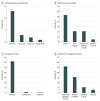
Results: A total of 309 patients had genomic epilepsy tests performed (mean [SD] age, 5.6 [0.8] years; 163 [52.8%] male), and 185 patients had a genetic variant reported. The reported variants resulted in 61 patients with and 124 patients without a genetic diagnosis (VUS variants only). On reinterpretation of all reported variants, 67 of the 185 patients (36.2%) had a change in variant classification. Of the 67 patients with a genetic variant change in interpretation, 21 (31.3%) experienced a change in diagnosis. During the 5 years of the study, 19 of 61 patients (31.1%) with a genetic diagnosis and 48 of 124 patients (38.7%) with undiagnosed conditions (VUS only) had their results reclassified. Review of genomic reports issued during the final 2 years of the study identified reclassification of variants in 4 of 16 patients (25.0%) with a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant and 11 of 41 patients (26.8%) with a VUS.
Conclusions and relevance: The identified high rate of reinterpretation in this study suggests that interpretation of genomic test results has rapidly evolved during the past 5 years. These findings suggest that reinterpretation of genomic test results should be performed at least every 2 years.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Comprehensive Epilepsy Panel GeneDx. https://www.genedx.com/test-catalog/available-tests/comprehensive-epilep.... Updated December 2016. Accessed May 2018.
-
- College of American Pathologists Sequence variants—interpretation and reporting In: Molecular Pathology Checklist: CAP Accreditation Program. Northfield, IL: College of American Pathologists; July 28, 2015.
-
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. ; ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee . Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17(5):405-424. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nambot S, Thevenon J, Kuentz P, et al. ; Orphanomix Physicians’ Group . Clinical whole-exome sequencing for the diagnosis of rare disorders with congenital anomalies and/or intellectual disability: substantial interest of prospective annual reanalysis. Genet Med. 2018;20(6):645-654. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.162 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

