Peripherally Restricted, Highly Potent, Selective, Aqueous-Soluble EP2 Antagonist with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- PMID: 30398879
- PMCID: PMC6633905
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00764
Peripherally Restricted, Highly Potent, Selective, Aqueous-Soluble EP2 Antagonist with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Abstract
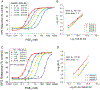
The prostaglandin E2 receptor, EP2, plays an important role in physiology and in a variety of pathological conditions. Studies indicate that EP2 is pro-inflammatory in chronic peripheral and central nervous system disease and cancer models. Thus, targeting the EP2 receptor with small molecules could be a therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory diseases and cancer. We recently reported a novel class of competitive antagonists of the EP2 receptor. However, earlier leads displayed low selectivity against the DP1 prostanoid receptor, moderate plasma half-life, and low aqueous solubility, which renders them suboptimal for testing in animal models of disease. We now report a novel compound TG8-69, which has suitable drug-like properties. We present synthesis, lead-optimization studies, pharmacological characterization, and anti-inflammatory properties of this compound that support its use in chronic peripheral inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, endometriosis, and cancer, in which EP2 appears to play a pathogenic role.
Keywords: EP2 antagonist; anti-inflammatory; aqueous-solubility; cytokines; lead-optimization; tetrazole.
Figures
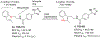
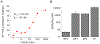
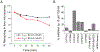

Similar articles
-
Potent, Selective, Water Soluble, Brain-Permeable EP2 Receptor Antagonist for Use in Central Nervous System Disease Models.J Med Chem. 2020 Feb 13;63(3):1032-1050. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01218. Epub 2020 Jan 16. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31904232 Free PMC article.
-
Lead optimization studies of cinnamic amide EP2 antagonists.J Med Chem. 2014 May 22;57(10):4173-84. doi: 10.1021/jm5000672. Epub 2014 May 5. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24773616 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of E-type prostanoid receptors 2 and 4 in microglia stimulated with lipopolysaccharide.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Jan 5;14(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0780-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28086956 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2-induced inflammation: Relevance of prostaglandin E receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1851(4):414-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25038274 Review.
-
Prostaglandin receptor EP2 in the crosshairs of anti-inflammation, anti-cancer, and neuroprotection.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Jul;34(7):413-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23796953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Second-Generation Prostaglandin Receptor EP2 Antagonist, TG8-260, with High Potency, Selectivity, Oral Bioavailability, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Jan 25;5(2):118-133. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00255. eCollection 2022 Feb 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35187419 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic nervous system and inflammation interaction in endometriosis-associated pain.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Mar 7;17(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01752-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32145751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EP2 Antagonists (2011-2021): A Decade's Journey from Discovery to Therapeutics.J Med Chem. 2021 Aug 26;64(16):11816-11836. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00816. Epub 2021 Aug 5. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34352171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Second-Generation EP2 Receptor Antagonist Reduces Neuroinflammation and Gliosis After Status Epilepticus in Rats.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Apr;18(2):1207-1225. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00969-5. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 33410110 Free PMC article.
-
Azaindole therapeutic agents.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Dec 15;28(24):115830. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115830. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33161343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Westman M; Korotkova M; af Klint E; Stark A; Audoly LP; Klareskog L; Ulfgren AK; Jakobsson PJ Expression of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum 2004, 50, 1774–80. - PubMed
-
- Myers LK; Kang AH; Postlethwaite AE; Rosloniec EF; Morham SG; Shlopov BV; Goorha S; Ballou LR The genetic ablation of cyclooxygenase 2 prevents the development of autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2000, 43, 2687–93. - PubMed
-
- Trebino CE; Stock JL; Gibbons CP; Naiman BM; Wachtmann TS; Umland JP; Pandher K; Lapointe JM; Saha S; Roach ML; Carter D; Thomas NA; Durtschi BA; McNeish JD; Hambor JE; Jakobsson PJ; Carty TJ; Perez JR; Audoly LP Impaired inflammatory and pain responses in mice lacking an inducible prostaglandin E synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 9044–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brodie MJ; Hensby CN; Parke A; Gordon D Is prostacyclin in the major pro-inflammatory prostanoid in joint fluid? Life Sci 1980, 27, 603–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

