Skeletal muscle interstitial fluid metabolomics at rest and associated with an exercise bout: application in rats and humans
- PMID: 30398905
- PMCID: PMC6417688
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00156.2018
Skeletal muscle interstitial fluid metabolomics at rest and associated with an exercise bout: application in rats and humans
Abstract
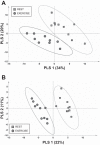
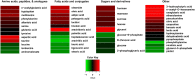
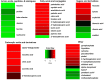
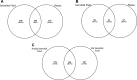
Blood or biopsies are often used to characterize metabolites that are modulated by exercising muscle. However, blood has inputs derived from multiple tissues, biopsies cannot discriminate between secreted and intracellular metabolites, and their invasive nature is challenging for frequent collections in sensitive populations (e.g., children and pregnant women). Thus, minimally invasive approaches to interstitial fluid (IF) metabolomics would be valuable. A catheter was designed to collect IF from the gastrocnemius muscle of acutely anesthetized adult male rats at rest or immediately following 20 min of exercise (~60% of maximal O2 uptake). Nontargeted, gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis was used to detect 299 metabolites, including nonannotated metabolites, sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, and purine metabolites and derivatives. Just 43% of all detected metabolites were common to IF and blood plasma, and only 20% of exercise-modified metabolites were shared in both pools, highlighting that the blood does not fully reflect the metabolic outcomes in muscle. Notable exercise patterns included increased IF amino acids (except leucine and isoleucine), increased α-ketoglutarate and citrate (which may reflect tricarboxylic acid cataplerosis or shifts in nonmitochondrial pathways), and higher concentration of the signaling lipid oleamide. A preliminary study of human muscle IF was conducted using a 20-kDa microdialysis catheter placed in the vastus lateralis of five healthy adults at rest and during exercise (65% of estimated maximal heart rate). Approximately 70% of commonly detected metabolites discriminating rest vs. exercise in rats were also changed in exercising humans. Interstitium metabolomics may aid in the identification of molecules that signal muscle work (e.g., exertion and fatigue) and muscle health.
Keywords: beta-oxidation; interstitium; metabolome.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel amino acid and metabolomics signature in mice overexpressing muscle uncoupling protein 3.FASEB J. 2017 Feb;31(2):814-827. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600914R. Epub 2016 Nov 10. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 27871066 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative metabolomics of muscle interstitium fluid in human trapezius myalgia: an in vivo microdialysis study.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013 Dec;113(12):2977-89. doi: 10.1007/s00421-013-2716-6. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24078209 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Exhaustive Exercise on Plasma Metabolic Profiles of Male and Female Rats.J Sports Sci Med. 2019 Jun 1;18(2):253-263. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2019. PMID: 31191095 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle amino acid metabolism at rest and during exercise: role in human physiology and metabolism.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1998;26:287-314. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1998. PMID: 9696993 Review.
-
The regulation of carbohydrate and fat metabolism during and after exercise.Front Biosci. 1998 Sep 15;3:D1011-27. doi: 10.2741/a342. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9740552 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning and multi-omics in precision medicine for ME/CFS.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 14;23(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05915-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39810236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eight-year diet and physical activity intervention affects serum metabolites during childhood and adolescence: A nonrandomized controlled trial.iScience. 2024 Jun 17;27(7):110295. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110295. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39055945 Free PMC article.
-
α-Ketoglutarate Is a Circulatory Exercise Factor That Promotes Learning and Memory Recall and Has Antidepressant Properties.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025 Mar 3;5(3):100477. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2025.100477. eCollection 2025 May. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 40248276 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise plasma metabolomics and xenometabolomics in obese, sedentary, insulin-resistant women: impact of a fitness and weight loss intervention.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Dec 1;317(6):E999-E1014. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00091.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 17. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31526287 Free PMC article.
-
Interindividual Variability in Postprandial Plasma Fructose Patterns in Adults.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 13;16(18):3079. doi: 10.3390/nu16183079. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339679 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

