Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- PMID: 30399208
- PMCID: PMC6517304
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006349.pub4
Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
Abstract
Background: Percutaneous vertebroplasty remains widely used to treat osteoporotic vertebral fractures although our 2015 Cochrane review did not support its role in routine practice.
Objectives: To update the available evidence of the benefits and harms of vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures.
Search methods: We updated the search of CENTRAL, MEDLINE and Embase and trial registries to 15 November 2017.
Selection criteria: We included randomised and quasi-randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of adults with painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures, comparing vertebroplasty with placebo (sham), usual care, or another intervention. As it is least prone to bias, vertebroplasty compared with placebo was the primary comparison. Major outcomes were mean overall pain, disability, disease-specific and overall health-related quality of life, patient-reported treatment success, new symptomatic vertebral fractures and number of other serious adverse events.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodologic procedures expected by Cochrane.
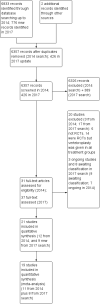
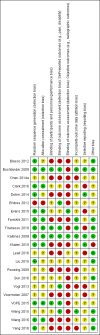
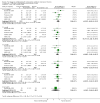
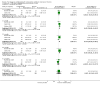
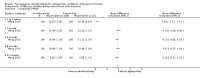
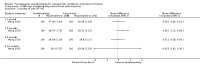
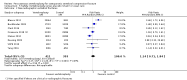
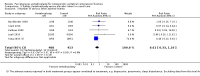
Main results: Twenty-one trials were included: five compared vertebroplasty with placebo (541 randomised participants), eight with usual care (1136 randomised participants), seven with kyphoplasty (968 randomised participants) and one compared vertebroplasty with facet joint glucocorticoid injection (217 randomised participants). Trial size varied from 46 to 404 participants, most participants were female, mean age ranged between 62.6 and 81 years, and mean symptom duration varied from a week to more than six months.Four placebo-controlled trials were at low risk of bias and one was possibly susceptible to performance and detection bias. Other trials were at risk of bias for several criteria, most notably due to lack of participant and personnel blinding.Compared with placebo, high- to moderate-quality evidence from five trials indicates that vertebroplasty provides no clinically important benefits with respect to pain, disability, disease-specific or overall quality of life or treatment success at one month. Evidence for quality of life and treatment success was downgraded due to possible imprecision. Evidence was not downgraded for potential publication bias as only one placebo-controlled trial remains unreported. Mean pain (on a scale zero to 10, higher scores indicate more pain) was five points with placebo and 0.7 points better (0.3 better to 1.2 better) with vertebroplasty, an absolute pain reduction of 7% (3% better to 12% better, minimal clinical important difference is 15%) and relative reduction of 10% (4% better to 17% better) (five trials, 535 participants). Mean disability measured by the Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire (scale range zero to 23, higher scores indicate worse disability) was 14.2 points in the placebo group and 1.5 points better (0.4 better to 2.6 better) in the vertebroplasty group, absolute improvement 7% (2% to 11% better), relative improvement 9% better (2% to 15% better) (four trials, 472 participants).Disease-specific quality of life measured by the Quality of Life Questionnaire of the European Foundation for Osteoporosis (QUALEFFO) (scale zero to 100, higher scores indicating worse quality of life) was 62 points in the placebo group and 2.3 points better (1.4 points worse to 6.7 points better), an absolute imrovement of 2% (1% worse to 6% better); relative improvement 4% better (2% worse to 10% better) (three trials, 351 participants). Overall quality of life (European Quality of Life (EQ5D), zero = death to 1 = perfect health, higher scores indicate greater quality of life) was 0.38 points in the placebo group and 0.05 points better (0.01 better to 0.09 better) in the vertebroplasty group, absolute improvement: 5% (1% to 9% better), relative improvement: 18% (4% to 32% better) (three trials, 285 participants). In one trial (78 participants), 9/40 (or 225 per 1000) people perceived that treatment was successful in the placebo group compared with 12/38 (or 315 per 1000; 95% CI 150 to 664) in the vertebroplasty group, RR 1.40 (95% CI 0.67 to 2.95), absolute difference: 9% more reported success (11% fewer to 29% more); relative change: 40% more reported success (33% fewer to 195% more).Low-quality evidence (downgraded due to imprecision and potential for bias from the usual-care controlled trials) indicates uncertainty around the risk estimates of harms with vertebroplasty. The incidence of new symptomatic vertebral fractures (from six trials) was 48/418 (95 per 1000; range 34 to 264)) in the vertebroplasty group compared with 31/422 (73 per 1000) in the control group; RR 1.29 (95% CI 0.46 to 3.62)). The incidence of other serious adverse events (five trials) was 16/408 (34 per 1000, range 18 to 62) in the vertebroplasty group compared with 23/413 (56 per 1000) in the control group; RR 0.61 (95% CI 0.33 to 1.10). Notably, serious adverse events reported with vertebroplasty included osteomyelitis, cord compression, thecal sac injury and respiratory failure.Our subgroup analyses indicate that the effects did not differ according to duration of pain (acute versus subacute). Including data from the eight trials that compared vertebroplasty with usual care in a sensitivity analyses altered the primary results, with all combined analyses displaying considerable heterogeneity.
Authors' conclusions: We found high- to moderate-quality evidence that vertebroplasty has no important benefit in terms of pain, disability, quality of life or treatment success in the treatment of acute or subacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures in routine practice when compared with a sham procedure. Results were consistent across the studies irrespective of the average duration of pain.Sensitivity analyses confirmed that open trials comparing vertebroplasty with usual care are likely to have overestimated any benefit of vertebroplasty. Correcting for these biases would likely drive any benefits observed with vertebroplasty towards the null, in keeping with findings from the placebo-controlled trials.Numerous serious adverse events have been observed following vertebroplasty. However due to the small number of events, we cannot be certain about whether or not vertebroplasty results in a clinically important increased risk of new symptomatic vertebral fractures and/or other serious adverse events. Patients should be informed about both the high- to moderate-quality evidence that shows no important benefit of vertebroplasty and its potential for harm.
Conflict of interest statement
R Buchbinder was a principal investigator of Buchbinder 2009. D Kallmes was a principal investigator of Kallmes 2009 and
Figures





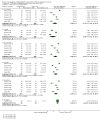
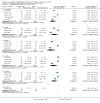


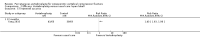



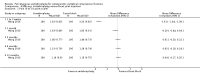
















Update of
-
Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 4;4(4):CD006349. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006349.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 06;11:CD006349. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006349.pub4. PMID: 29618171 Free PMC article. Updated.
Comment in
-
Benefits and Harms of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Cochrane Review Summary With Commentary.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019 Dec;98(12):1151-1152. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000001274. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 31490184 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Blasco 2012 {published data only}
-
- Blasco J, Martinez‐Ferrer A, Macho J, San Roman L, Pomes J, Carrasco J, et al. Effect of vertebroplasty on pain relief, quality of life, and the incidence of new vertebral fractures: a 12‐month randomized follow‐up, controlled trial. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2012;27(5):1159‐66. - PubMed
-
- Blasco J, Martinez‐Ferrer A, San Roman J, Macho A, Lopez Rueda D, Campodonico C, et al. Risk factors for the development of chronic back pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty. European Society of Radiology. 2014.
-
- Peris P, Blasco J, Carrasco JL, Martinez‐Ferrer A, Macho J, San Roman L, et al. Risk factors for the development of chronic back pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment. Calcified Tissue International 2015;96(2):89‐96. - PubMed
Buchbinder 2009 {published data only}
-
- Buchbinder R, Osborne RH, Ebeling PR, Wark JD, Mitchell P, Wriedt C, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures.[see comment]. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361(6):557‐68. - PubMed
-
- Kroon F, Staples MP, Ebeling P, Wark J, Osborne R, Mitchell P, et al. Vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures: Two‐year results from a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2014;29(6):1346‐55. - PubMed
Chen 2014a {published data only}
-
- Chen D, An ZQ, Song S, Tang JF, Qin H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with conservative treatment in patients with chronic painful osteoporotic spinal fractures. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2014;21:473‐7. - PubMed
Clark 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bird P, Clark W, Diamond T, Schlaphoff G, Smerdely P, Gonski P, et al. A placebo controlled trial of vertebral fill technique vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic fracture (VAPOUR trial). Arthritis and Rheumatology. Conference: American College of Rheumatology/Association of Rheumatology Health Professionals Annual Scientific Meeting. 2016; Vol. 68:413‐4.
-
- Clark W, Bird P, Gonski P, Diamond T, Smerdely P, McNeil H, et al. Safety and efficacy of vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic fractures (VAPOUR): a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388(10052):1408‐16. - PubMed
Dohm 2014 {published data only}
Endres 2012 {published data only}
-
- Endres S, Badura A. Shield kyphoplasty through a unipedicular approach compared to vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty in osteoporotic thoracolumbar fracture: A prospective randomized study. Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research 2012;98(3):334‐40. - PubMed
Evans 2015 {published data only}
-
- Evans A, Kip K, Brinjikji W, Layton K, Jensen M, Gaughen J, et al. Randomized controlled trial of vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Journal of Neurointerventional Surgery 2015;8(7):756‐63. - PubMed
Farrokhi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Farrokhi MR, Alibai E, Maghami Z. Randomized controlled trial of percutaneous vertebroplasty versus optimal medical management for the relief of pain and disability in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Journal of Neurosurgery. Spine 2011;14(5):561‐9. - PubMed
Firanescu 2018 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Firanescu C, Lohle PN, Vries J, Klazen CA, Juttmann JR, Clark W, et al. VERTOS IV study group. A randomised sham controlled trial of vertebroplasty for painful acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures (VERTOS IV). Trials 2011;12(93):http://www.trialsjournal.com/content/12/1/93. [DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-93] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Firanescu C, Vries J, Lodder P, Schoemaker MC, Smeets AJ, Vemans A, et al. VERTOS IV study group. American Society Spine Radiology (ASSR) 2017 Annual Symposium. San Diego, 2017.
-
- Firanescu CE, Vries J, Lodder P, Venmans A, Shoemaker MC, Smeet AJ, Donga E, Juttmann JR, Klazen CAH, Elgersma OEH, Jansen FH, Tielbeek AV, Boukrab I, Schonenberg K, Rooij WJJ, Hirsch JA, Lohle PNM. Vertebroplasty versus sham procedure for painful acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (VERTOS IV): randomised sham controlled clinical trial. BMJ 2018 2018;360:k1551. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.k1551] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Kallmes 2009 {published data only}
-
- Brinjikji W, Comstock BA, Heagerty PJ, Jarvik JG, Kallmes DF. Investigational Vertebroplasty Efficacy and Safety Trial: detailed analysis of blinding efficacy. Radiology 2010;257(1):219‐25. - PubMed
Klazen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Klazen CA, Lohle PN, Vries J, Jansen FH, Tielbeek AV, Blonk MC, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open‐label randomised trial. Lancet 2010;376(9746):1085‐92. [PUBMED: 20701962] - PubMed
-
- Klazen CA, Verhaar HJ, Lampmann LE, Juttmann JR, Blonk MC, Jansen FH, et al. VERTOS II: percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative therapy in patients with painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures; rationale, objectives and design of a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Trials 2007;8:33. [PUBMED: 17973983] - PMC - PubMed
Leali 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Leali PT, Solla F, Maestretti G, Balsano M, Doria C. Safety and efficacy of vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A prospective multicenter international randomized controlled study. Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism 2016;13(3):234‐6. - PMC - PubMed
Liu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Liu JT, Li CS, Chang CS, Liao WJ. Long‐term follow‐up study of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture treated using balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Journal of Neurosurgery Spine 2015;23(1):94‐8. - PubMed
-
- Liu JT, Liao WJ, Tan WC, Lee JK, Liu CH. Balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a prospective, comparative, and randomized clinical study. Osteoporosis International 2010;21:359–64. - PubMed
Rousing 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rousing R, Andersen MO, Jespersen SM, Thomsen K, Lauritsen J, Rousing Rikke, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared to conservative treatment in patients with painful acute or subacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: three‐months follow‐up in a clinical randomized study. Spine 2009;34(13):1349‐54. - PubMed
-
- Rousing R, Hansen KL, Andersen MO, Jespersen SM, Thomsen K, Lauritsen JM. Twelve‐months follow‐up in forty‐nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated conservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty: a clinical randomized study. Spine 2010;35(5):478‐82. [PUBMED: 20190623] - PubMed
Sun 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sun K, Liu Y, Peng H, Tan JF, Zhang M, Zheng XN, et al. A comparative study of high‐viscosity cement percutaneous vertebroplasty vs. low‐viscosity cement percutaneous kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Medical Sciences 2016;36(3):389‐94. - PubMed
Vogl 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vogl TJ, Pflugmacher R, Hierholzer J, Stender G, Gounis M, Wakhloo A, et al. Cement directed kyphoplasty reduces cement leakage as compared with vertebroplasty: results of a controlled, randomized trial. Spine 2013;38(20):1730‐6. - PubMed
Voormolen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Voormolen MH, Lohle PN, Fransen H, Juttmann JR, Waal Malefijt J, Lampmann LE. [Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: first short term results]. Nederlands Tijdschrift Voor Geneeskunde 2003;147(32):1549‐53. - PubMed
-
- Voormolen MH, Lohle PN, Juttmann JR, Graaf Y, Fransen H, Lampmann LE. The risk of new osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the year after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology 2006;17(1):71‐6. - PubMed
-
- Voormolen MH, Lohle PN, Lampmann LE, Wildenberg W, Juttmann JR, Diekerhof CH, et al. Prospective clinical follow‐up after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology 2006;17(8):1313‐20. - PubMed
-
- Voormolen MH, Mali WP, Lohle PN, Fransen H, Lampmann LE, Graaf Y, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with optimal pain medication treatment: short‐term clinical outcome of patients with subacute or chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. The VERTOS study. American Journal of Neuroradiology 2007;28(3):555‐60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Voormolen MH, Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M, Graaf Y, Lampmann LE, Lohle PN, et al. Pain response in the first trimester after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with or without bone marrow edema. AJNR: American Journal of Neuroradiology 2006;27(7):1579‐85. - PMC - PubMed
VOPE 2015 {unpublished data only}
-
- Hansen EJ. A double‐blind randomized clinical study comparing vertebroplasty with a SHAM procedure for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (VOPE). Thesis, University of Southern Denmark: Center for Spine Surgery and Research, Middelfart Hospital and Institute of Regional Health Research, University of Southern Denmark, Denmark 2015.
-
- Hansen EJ, Simony A, Rousing R, Carreon LY, Tropp H, Andersen MO. Double blind placebo‐controlled trial of percutaneous vertebroplasty (VOPE). Global Spine Journal. 2017; Vol. 6 Issue 1_suppl:s‐0036‐1582763. [DOI: ]
-
- NCT01537770. Vertebroplasty versus periost infiltration with lidocaine as pain treatment in osteoporotic fractures in the thoracic and lumbar spine. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01537770 Trial registered: EUCTR 2010‐024050‐10 (Also NCT01537770) completed as of 11 September 2015.
Wang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wang C, Ma J, Zhang C, Nie L. Comparison of high‐viscosity cement vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Physician 2015;18(2):187‐94. - PubMed
Wang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Hao D, Guo H, Wang B, Wang X. Treatment for acute or subacute osteoporosis vertebral compression fractures: Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus facets blocking (a clinical randomized study). European Spine Journal; http://eposterlyon.eurospine.org/cm_data/eposter/P17.PDF. 2014; Vol. 23, Issue 5:Supplement, pp 527‐557.
-
- Hao D, Wang B, Guo H, Wang X. Treatment for acute or subacute osteoporosis vertebral compression fractures: Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus facets blocking (a clinical randomized study). European Spine Journal 2014;23(1):S533.
-
- Wang B, Guo H, Yuan L, Huang D, Zhang H, Hao D. A prospective randomized controlled study comparing the pain relief in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with the use of vertebroplasty or facet blocking. European Spine Journal 2016;25:3486‐94. [DOI: 10.1007/s00586-016-4425-4] - DOI - PubMed
Yang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yang EZ, Xu JG, Huang GZ, Xiao WZ, Liu XK, Zeng BF, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in aged patients with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 2016;41(8):653‐60. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Cai 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cai J, Hao YW, Li C, Yang HQ. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with bone cement injection for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures via transpedicular approach [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 2015;19(30):4892‐7.
Chen 2014b {published data only}
-
- Chen C, Bian J, Zhang W, Zhao C, Wei H. Unilateral versus bilateral vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques 2014;27(8):E301‐4. - PubMed
Chun‐lei 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chen‐lei L, Yi‐he H, Gui‐qing W, Yong‐zhi T, Xiang‐jiang W, Han‐tao H. Curative effects of unipedicular and bipedicular vertebroplasty in treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the elderly population. Journal of Xi'an Jiatong University 2015;36:6.
Du 2014 {published data only}
-
- Du J, Li X, Lin X. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: two‐year follow‐up in a prospective controlled study. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica 2014;80(4):477‐86. - PubMed
Gilula 2013 {published data only}
Gu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Gu YT, Zhu DH, Liu HF, Zhang F, McGuire R. Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for preventing secondary fracture after vertebroplasty. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2015;10:31 doi: 10.1186/s13018‐015‐0172‐1. [DOI: 10.1186/s13018-015-0172-1] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Huang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Huang XN. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: High‐viscosity versus low‐viscosity bone cement [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 2014;18(16):2461‐7.
Li 2015a {published data only}
-
- Li J, Shen WL, Chang XH. Comparison of clinical effects between unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. [Chinese]. Journal of Dalian Medical University 2015;37(2):145‐7.
Liu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Liu CL, Hu YH, Wang GQ, Tang YZ, Wang XJ, Hou HT. Curative effects of unipedicular and bipedicular vertebroplasty in treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the elderly population. [Chinese]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University (Medical Sciences) 2015;36(6):857‐61.
Min 2015 {published data only}
-
- Min P, Zhang YP, Cao H. CT‐guided bone cement injection combined with artificial tiger bone meal to repair osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: Callus growth and bone healing [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 2015;19(3):335‐9.
Son 2014 {published data only}
Xiao‐nan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Xiao‐nan H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: high viscosity versus low‐viscosity bone cement. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 2014;18(16):2461‐7.
Yang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yang DH, Cho KH, Chung YS, Kim YR. Effect of vertebroplasty with bone filler device and comparison with balloon kyphoplasty. European Spine Journal 2014;23(12):2718‐25. - PubMed
Yi 2014 {published data only}
Yi 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yi HJ, Jeong JH, Im SB, Lee JK. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment for one level thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: results of an over 2‐year follow‐up. Pain Physician 2016;19(5):E743‐50. - PubMed
Ying 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ying L. Chen Z, Yang G. Clinical study of high viscosity bone cement in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Biomedical Research (India) 2017;28(18):7837‐40.
Yokoyama 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yokoyama K, Kawanishi M, Yamada M, Tanaka H, Ito Y, Kawabata S, et al. Comparison of vertebroplasty versus vertebral perforation for the treatment of acute vertebral compression fractures. Turkish Neurosurgery 2016;26(3):423‐9. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama K, Kawanishi M, Yamada M, Tanaka H, Ito Y, Kuroiwa T. Long‐term therapeutic effects of vertebroplasty for painful vertebral compression fracture: a retrospective comparative study. British Journal of Neurosurgery 2017;31(2):184‐8. - PubMed
Zhang 2015a {published data only}
-
- Zhang L, Wang J, Feng X, Tao Y, Yang J, Wang Y, et al. A comparison of high viscosity bone cement and low viscosity bone cement vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 2015;129:10‐6. - PubMed
Zhang 2015b {published data only}
Zhang 2015c {published data only}
-
- Zhang L, Gu X, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Cai X, Tao K. Unilateral or bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for acute osteoporotic vertebral fracture: a prospective study. Journal of Spine Disorders & Techniques 2015; Vol. 28, issue 2:85‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Chen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chen JP, Qi XW, Li SJ, Kuang LP, Yuan XH, Wang GS, et al. Bone cement injection as vertebral augmentation therapy for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 2015;19(21):3292‐6. [DOI: ]
Dolin 2003 {unpublished data only}
-
- Doin S. A randomised controlled trial of vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral crush fractures. http://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN14442024 (first received 12 September 2003) Trial completed.
Laredo (OSTEO‐6) {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00749060. Prospective randomized comparative study of balloon kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty and conservative management in acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures of less than 6 weeks. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00749060 (first received September 8, 2008) Trial completed June 2012.
Laredo (STIC2) {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00749086. Prospective randomized study of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in subacute (older than 6 weeks) osteoporotic vertebral fractures (STIC2). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00749086 Trial registered: NCT00749086. Recruitment commenced Dec 2007. Trial completed June 2012.
Li 2015b {published data only}
-
- Li DH, Liu XW, Peng XT, Wang ZG, Wang BC, Jin P, et al. Bone filling mesh container for treatment of vertebral compression fractures can reduce the leakage of bone cement. [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 15 Jan 2015;19(3):358‐3.
Sorensen 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00203554. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment of pain: a prospective, randomized controlled study of osteoporotic fractures in the spine. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00203554 (first received 16 September 2005).
Tan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Tan B, Liu XW, Liu G, Li YS, Qin ZJ, Yang CP. Percutaneous kyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A randomized comparison [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 2016;20(4):539‐43.
Zhou 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zhou W. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with high‐viscosity bone cement for treatment of severe osteoporotic thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures [Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research 2015;19(46):7534‐8.
References to ongoing studies
Longo 2010 {unpublished data only}
-
- Longo UG, Loppini M, Denaro L, Brandi ML, Maffulli N, Denaro V. The effectiveness and safety of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. A double blind, prospective, randomized, controlled study. Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism : the official journal of the Italian Society of Osteoporosis, Mineral Metabolism, and Skeletal Diseases 2010;7(2):109‐13. [PUBMED: 22460014] - PMC - PubMed
Sun 2012 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01677806. Investigational percutaneous vertebroplasty efficacy and safety trial. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01677806 (first received 23 August 2012).
VERTOS V {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01963039. A trial of vertebroplasty for painful chronic osteoporotic vertebral fractures (VERTOS V). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01963039 First registered 28 August 2013.
Additional references
Al‐Nakshabandi 2011
Amin 2014
Anderson 2013
-
- Anderson PA, Froyshteter AB, Tontz WL Jr. Meta‐analysis of vertebral augmentation compared with conservative treatment for osteoporotic spinal fractures. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2013;28(2):378‐32. - PubMed
Baumann 2006
-
- Baumann A, Tauss J, Baumann G, Tomka M, Hessinger M, Tiesenhausen K. Cement embolization into the vena cava and pulmonal arteries after vertebroplasty: interdisciplinary management. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery 2006;31(5):558‐61. - PubMed
Belkoff 2001
-
- Belkoff S, Mathis JM, Jasper LE, Deramond H. The biomechanics of vertebroplasty: The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine 2001;26(14):1537‐41. - PubMed
Bijur 2003
-
- Bijur PE, Latimer CT, Gallagher EJ. Validation of a verbally administered numerical rating scale of acute pain for use in the emergency department. Academic Emergency Medicine 2003;10:390‐2. - PubMed
Birnbaumer 2003
-
- Birnbaumer DM. Visual Analog Scale vs. Numerical Rating Scale: Much Ado About Nothing?. NEJM Journal Watch. Available from: https://www.jwatch.org/em200305140000005/2003/05/14/visual‐analog‐scale‐... 2013.
Bliemel 2012
-
- Bliemel C, Oberkircher L, Buecking B, Timmesfeld N, Ruchholtz S, Krueger A. Higher incidence of new vertebral fractures following percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty‐‐fact or fiction?. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica 2012;78(2):220‐9. - PubMed
Bono 2010
-
- Bono C, Heggeness M, Mick C, Resnick D, Watters, WC 3rd. North American SpineSociety: newly released vertebroplasty randomized controlled trials: a tale of two trials. Spine Journal 2010;10(3):238‐40. - PubMed
Caynak 2009
-
- Caynak B, Onan B, Sagbas E, Duran C, Akpinar B. Cardiac tamponade and pulmonary embolism as a complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2009;87(1):299‐301. - PubMed
Chen 2013
-
- Chen AT, Cohen DB, Skolasky RL. Impact of nonoperative treatment, vertebroplasty, and kyphoplasty on survival and morbidity after vertebral compression fracture in the Medicare population. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. American volume 2013;95(19):1729‐36. - PubMed
Chosa 2011
-
- Chosa K, Naito A, Awai K. Newly developed compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: comparison with conservative treatment. Japanese Journal of Radiology 2011;29(5):335‐41. - PubMed
Comstock 2013
Damaskinos 2015
-
- Damaskinos M. Study about the effect of preventive adjacent level cement augmentation after osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT0248925 (first received 25 June 2015) 2015.
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Ebrahim 2013
-
- Ebrahim S, Akl EA, Mustafa RA, Sun X, Walter SD, Heels‐Ansdell D, et al. Addressing continuous data for participants excluded from trial analysis: a guide for systematic reviewers. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(9):1014‐21. - PubMed
Eck 2008
-
- Eck JC, Nachtigall D, Humphreys SC, Hodges SD. Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta‐analysis of the literature. Spine Journal 2008;8(3):488‐97. - PubMed
Edidin 2011
-
- Edidin AA, Ong KL, Lau E, Kurtz SM. Mortality risk for operated and nonoperated vertebral fracture patients in the Medicare population. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2011;26(7):1617‐26. - PubMed
François 2003
-
- François K, Taeymans Y, Poffyn B, Nooten G. Successful management of a large pulmonary cement embolus after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine 2003;28(29):E424‐5. - PubMed
Galibert 1987
-
- Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Gars D. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty [Note preliminaire sur le traitement des angiomes vertebraux par vertebroplastie acrylique percutanee.]. Neuro‐Chirurgie 1987;33(2):166‐8. [PUBMED: 3600949] - PubMed
Genant 1993
-
- Genant HK, Wu CY, Kuijk C, Nevitt MC. Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research 1993;8(9):1137‐48. [PUBMED: 8237484] - PubMed
Gill 2007
-
- Gill JB, Kuper M, Chin PC, Zhang Y, Schutt R Jr. Comparing pain reduction following kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Physician 2007;10(4):583‐90. - PubMed
Gray 2007a
-
- Gray D, Hollingworth W, Onwudiwe N, Deyo RA, Jarvik JG. Thoracic and lumbar vertebroplasties performed in US Medicare enrollees, 2001‐2005. JAMA 2007;298(15):1760‐2. - PubMed
Grotle 2004
-
- Grotle M, Brox JI, Vøllestad NK. Concurrent comparison of responsiveness in pain and functional status measurements used for patients with low back pain. Spine 2004;29:E492‐E501. - PubMed
Han 2011
Hernlund 2013
Hide 2004
-
- Hide IG, Gangi A. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: history, technique and current perspectives. Clinical Radiology 2004;59(6):461‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011).
Hochmuth 2006
-
- Hochmuth K, Proschek D, Schwarz W, Mack M, Kurth AA, Vogl TJ. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the therapy of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a critical review. European Radiology 2006;16(5):998‐1004. [PUBMED: 16395532] - PubMed
Hulme 2006
-
- Hulme PA, Krebs J, Ferguson SJ, Berlemann U. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine 2006;31(17):1983‐2001. - PubMed
Kanis 1999
-
- Kanis JA, Johnell O. The burden of osteoporosis. Journal of Endocrinological Investment 1999;22:583‐8. - PubMed
Kanis 2000
-
- Kanis JA, Johnell O, Oden A, Sernbo I, Redlund‐Johnell I, Dawson A, et al. Long‐term risk of osteoporotic fracture in Malmo. Osteoporosis International 2000;11(8):669‐774. - PubMed
Kim 2014
-
- Kim SP, Son BS, Lee SK, Kim DH. Cardiac perforation due to intracardiac bone cement after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Journal of Cardiac Surgery 2014;29(4):499‐500. - PubMed
Kroon 2014
-
- Kroon F, Staples MP, Ebeling P, Wark J, Osborne R, Mitchell P, et al. Vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures: Two‐year results from a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2014;29(6):1346‐55. - PubMed
Lad 2009
-
- Lad SP, Patil CG, Lad EM, Hayden MG, Boakye M. National trends in vertebral augmentation procedures for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Surgical Neurology 2009;71(5):580‐4. - PubMed
Lange 2014
-
- Lange A, Kasperk C, Alvares L, Sauermann S, Braun S. Survival and cost comparison of kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty using German claims data. Spine 2014;39(4):318‐26. - PubMed
Lau 2008
-
- Lau E, Ong KL, Kurtz SM, Schmier J, Edidin AA. Mortalityfollowing the diagnosis of a vertebral compression fracture in theMedicare population. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. American volume 2008;90(7):1479‐86. - PubMed
Leake 2011
Lee 2009
-
- Lee MJ, Dumonski M, Cahill P, Stanley T, Park D, Singh K. Percutaneous treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta‐analysis of complications. Spine 2009;34(11):1228‐32. - PubMed
Leslie 2011
-
- Leslie WD, Sadatsafavi M, Lix LM, Azimaee M, Morin S, Metge CJ, et al. Secular decreases in fracture rates 1986–2006 for Manitoba, Canada: a population‐based analysis. Osteoporosis International 2011;22:2137‐43. - PubMed
Lips 1999
-
- Lips P, Cooper C, Agnusdei D, Caulin F, Egger P, Johnell O, et al. Quality of life in patients with vertebral fractures: validation of the Quality of Life Questionnaire of the European Foundation for Osteoporosis (QUALEFFO). Osteoporosis International 1999;10:150‐60. - PubMed
Liu 2013
-
- Liu J, Li X, Tang D, Cui X, Li X, Yao M, et al. Comparing pain reduction following vertebroplasty and conservative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Physician 2013;16(5):455‐64. - PubMed
Ma 2012
McCullough 2013
McDonald 2011
McGirt 2009
-
- McGirt MJ, Parker SL, Wolinsky JP, Witham TF, Bydon A, Gokaslan ZL. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: an evidenced‐based review of the literature. Spine Journal 2011;9(6):501‐8. [PUBMED: 19251485] - PubMed
Melton 1997
-
- Melton LJ 3rd, Thamer M, Ray NF, Chan JK, Chesnut CH 3rd, Einhorn TA, et al. Fractures attributable to osteoporosis: report from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 1997;12(1):16‐23. - PubMed
Monticelli 2005
-
- Monticelli F, Meyer HJ, Tutsch‐Bauer E. Fatal pulmonary cement embolism following percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP). Forensic Science International 2005;149(1):35‐8. - PubMed
Mundano 2009
Nakstad 2008
-
- NCT00635297. Percutaneous vertebroplasty. Study of refracture rates after prophylactic vertebroplasty of adjacent vertebrae. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00635297 (first received 5 March 2008).
Nieuwenhuijse 2012
-
- NTR3282. Viscosity of PMMA bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a randomized controlled trial. http://www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=3282 14 Feb 2012.
Oudshoorn 2012
-
- Oudshoorn C, Hartholt KA, Zillikens MC, Panneman MJ, Velde N, Colin EM, et al. Emergency department visits due to vertebral fractures in the Netherlands, 1986–2008: steep increase in the oldest old, strong association with falls. Injury 2012;43(4):458‐61. - PubMed
Papanastassiou 2012
-
- Papanastassiou ID, Phillips FM, Meirhaeghe J, Berenson JR, Andersson GB, Chung G, et al. Comparing effects of kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, and non‐surgical management in a systematic review of randomized and non‐randomized controlled studies. European Spine Journal 2012;21(9):1826‐43. - PMC - PubMed
Ploeg 2006
-
- Ploeg WT, Veldhuizen AG, The B, Sietsma MS. Percutaneous vertebroplasty as a treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review. European Spine Journal 2006;15(12):1749‐58. - PubMed
Robinson 2012
-
- Robinson Y, Olerud C. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty—a systematic review of cement augmentation techniques for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures compared to standard medical therapy. Maturitas 2012;72:42‐9. - PubMed
Savović 2012
-
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157(6):429‐38. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Seo 2005
-
- Seo JS, Kim YJ, Choi BW, Kim TH, Choe KO. MDCT of pulmonary embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology 2005;184(4):1364‐5. - PubMed
Shi 2012
Staples 2011
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D (editors). Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Stevenson 2014
-
- Stevenson M, Gomersall T, Lloyd Jones M, Rawdin A, Hernandez M, Dias S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and cost‐effectiveness analysis. Health Technology Assessment (Winchester, England) 2014;18(17):1‐290. - PMC - PubMed
Ström 2011
-
- Ström O, Borgström F, Kanis JA, Compston J, Cooper C, McCloskey EV, et al. Osteoporosis: burden, health care provision and opportunities in the EU: a report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA). Archives of Osteoporosis 2011;6:59‐155. - PubMed
Syed 2006
Tang 2011
-
- Tang H, Zhao J, Hao C. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: surgery versus non‐operative management. Journal of International Medical Research 2011;39(4):1438‐47. - PubMed
Taylor 2006
-
- Taylor RS, Taylor RJ, Fritzell P. Balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fractures: a comparative systematic review of efficacy and safety. Spine 2006;31(23):2747‐55. - PubMed
Trout 2005
Trout 2006
Trout 2006a
Walters 2005
-
- Walters SJ, Brazier JE. Comparison ofthe minimally important difference for two health state utility measures: EQ‐5Dand SF‐6D. Quality of Life Research 2005;14(6):1523‐32. - PubMed
Wang 2012
Xing 2013
-
- Xing D, Ma JX, Ma XL, Wang J, Xu WG, Chen Y, et al. A meta‐analysis of balloon kyphoplasty compared to percutaneous vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2013;20(6):795‐803. - PubMed
Zampini 2010
Zhang 2013
-
- Zhang YZ, Kong LD, Cao JM, Ding WY, Shen Y. Incidence of subsequent vertebral body fractures after vertebroplasty. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2014;21(8):1292‐7. - PubMed
Zhao 2014
-
- Zhao J, Liu B. ChiCTR‐TRC‐14004835. A clinical trial of percutaneous vertebroplasty with high viscosity bone cement. 23 June 2014. Trial pending. chictr.org/en/proj/show.aspx?proj=8628.
Zou 2012
-
- Zou J, Mei X, Zhu X, Shi Q, Yang H. The long‐term incidence of subsequent vertebral body fracture after vertebral augmentation therapy: a systemic review and meta‐analysis. Pain Physician 2012;15(4):E515‐22. - PubMed
Álvarez 2006
-
- Álvarez L, Alcarez M, Pérez‐Higueras A, Granizo JJ, Miguel I, Rossi RE, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: Functional improvement in patients with osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 2006;31:1113‐8. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Buchbinder 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

