Mechanical Stretching Simulates Cardiac Physiology and Pathology through Mechanosensor Piezo1
- PMID: 30400259
- PMCID: PMC6262272
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm7110410
Mechanical Stretching Simulates Cardiac Physiology and Pathology through Mechanosensor Piezo1
Abstract
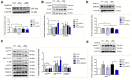
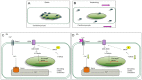
The dynamics of a living body enables organs to experience mechanical stimulation at cellular level. The human cardiomyocytes cell line provides a source for simulating heart dynamics; however, a limited understanding of the mechanical stimulation effect on them has restricted potential applications. Here, we investigated the effect of mechanical stimulation on the cardiac function-associated protein expressions in human cardiomyocytes. Human cardiomyocyte cell line AC16 was subjected to different stresses: 5% mild and 25% aggressive, at 1 Hz for 24 h. The stretched cardiomyocytes showed down-regulated Piezo1, phosphorylated-Ak transforming serine473 (P-AKTS473), and phosphorylated-glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta serine9 P-GSK3βS9 compared to no stretch. In addition, the stretched cardiomyocytes showed increased low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6), and phosphorylated-c-Jun N-terminal kinase threonine183/tyrosine185 (P-JNKT183/Y185). When Piezo inhibitor was added to the cells, the LRP6, and P-JNKT183/Y185 were further increased under 25%, but not 5%, suggesting that higher mechanical stress further activated the wingless integrated-(Wnt)-related signaling pathway when Piezo1 was inhibited. Supporting this idea, when Piezo1 was inhibited, the expression of phosphorylated-endothelial nitric oxide synthase serine1177 (P-eNOSS1177) and release of calcium ions were reduced under 25% compared to 5%. These studies demonstrate that cyclic mechanical stimulation affects cardiac function-associated protein expressions, and Piezo1 plays a role in the protein regulation.
Keywords: Piezo1; cardiomyocytes; mechanical stimulation; stretching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Mechanical stretch induces endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene expression in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009 May;36(5-6):559-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.05100.x. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19673940
-
Mechanical stretch triggers rapid epithelial cell division through Piezo1.Nature. 2017 Mar 2;543(7643):118-121. doi: 10.1038/nature21407. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28199303 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the mechanism of excessive apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells induced by shRNA-Piezo1 under abnormal mechanical stretch stress.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar;120(3):3989-3997. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27683. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30260030
-
Nitric Oxide and Mechano-Electrical Transduction in Cardiomyocytes.Front Physiol. 2020 Dec 15;11:606740. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.606740. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33384614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
Cited by
-
Channelling the Force to Reprogram the Matrix: Mechanosensitive Ion Channels in Cardiac Fibroblasts.Cells. 2021 Apr 23;10(5):990. doi: 10.3390/cells10050990. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33922466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piezo1 Channel Activation Reverses Pulmonary Artery Vasoconstriction in an Early Rat Model of Pulmonary Hypertension: The Role of Ca2+ Influx and Akt-eNOS Pathway.Cells. 2022 Jul 30;11(15):2349. doi: 10.3390/cells11152349. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35954193 Free PMC article.
-
Multiallelic rare variants support an oligogenic origin of sudden cardiac death in the young.Herz. 2021 Apr;46(Suppl 1):94-102. doi: 10.1007/s00059-019-04883-1. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Herz. 2021. PMID: 31970460 English.
-
Roles of Mechanosensitive Channel Piezo1 in Wound Healing and Scar Formation.Life (Basel). 2024 Mar 13;14(3):377. doi: 10.3390/life14030377. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piezo1 channel activation in response to mechanobiological acoustic radiation force in osteoblastic cells.Bone Res. 2021 Mar 10;9(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41413-020-00124-y. Bone Res. 2021. PMID: 33692342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King T.C. Elsevier’s Integrated Pathology. Mosby; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2007. Cardiovascular Pathology; pp. 169–195.
-
- Fiorillo C., Nediani C., Ponziani V., Giannini L., Celli A., Nassi N., Formigli L., Perna A.M., Nassi P. Cardiac volume overload rapidly induces oxidative stress-mediated myocyte apoptosis and hypertrophy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2005;1741:173–182. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2005.03.015. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

