Dietary Nitrate from Beetroot Juice for Hypertension: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 30400267
- PMCID: PMC6316347
- DOI: 10.3390/biom8040134
Dietary Nitrate from Beetroot Juice for Hypertension: A Systematic Review
Abstract
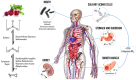
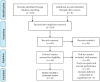
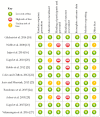
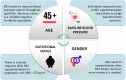
According to current therapeutic approaches, a nitrate-dietary supplementation with beetroot juice (BRJ) is postulated as a nutritional strategy that might help to control arterial blood pressure in healthy subjects, pre-hypertensive population, and even patients diagnosed and treated with drugs. In this sense, a systematic review of random clinical trials (RCTs) published from 2008 to 2018 from PubMed/MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, and manual searches was conducted to identify studies examining the relationship between BRJ and blood pressure. The specific inclusion criteria were: (1) RCTs; (2) trials that assessed only the BRJ intake with control group; and (3) trials that reported the effects of this intervention on blood pressure. The search identified 11 studies that met the inclusion criteria. This review was able to demonstrate that BRJ supplementation is a cost-effective strategy that might reduce blood pressure in different populations, probably through the nitrate/nitrite/nitric oxide (NO₃-/NO₂-/NO) pathway and secondary metabolites found in Beta vulgaris. This easily found and cheap dietary intervention could significantly decrease the risk of suffering cardiovascular events and, in doing so, would help to diminish the mortality rate associated to this pathology. Hence, BRJ supplementation should be promoted as a key component of a healthy lifestyle to control blood pressure in healthy and hypertensive individuals. However, several factors related to BRJ intake (e.g., gender, secondary metabolites present in B. vulgaris, etc.) should be studied more deeply.
Keywords: Beta vulgaris; blood pressure; dietary supplements; hypertension; nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
D.A.B.O. serves as a science product manager and scientific consultant for companies who sell dietary supplements in Europe (MTX Corporation®) and Colombia (Healthy Sports®). S.V. has served as professional advisor in dietary supplements industry in Spain. The remaining investigators have no competing interests to declare. This review does not constitute endorsement by the authors and/or the institution concerning the nutrients reviewed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Oral Supplementation With Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension-Results From BEET-PAH, an Exploratory Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study.J Card Fail. 2018 Oct;24(10):640-653. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Card Fail. 2018. PMID: 30244181 Clinical Trial.
-
Beetroot juice lowers blood pressure and improves endothelial function in pregnant eNOS-/- mice: importance of nitrate-independent effects.J Physiol. 2020 Sep;598(18):4079-4092. doi: 10.1113/JP279655. Epub 2020 May 27. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32368787
-
Effects of beetroot juice on blood pressure in hypertension according to European Society of Hypertension Guidelines: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2024 Oct;34(10):2240-2256. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2024.06.009. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 39069465
-
Effects of supervised exercise and dietary nitrate in older adults with controlled hypertension and/or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Nitric Oxide. 2017 Sep 30;69:78-90. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 23. Nitric Oxide. 2017. PMID: 28549665 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of dietary inorganic nitrate for lowering blood pressure in hypertensive adults: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019 Mar;17(3):365-389. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003842. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019. PMID: 30870330
Cited by
-
Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements for Older Adults with Long COVID-19.Clin Geriatr Med. 2022 Aug;38(3):565-591. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2022.04.004. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Clin Geriatr Med. 2022. PMID: 35868674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cardioprotective Role of Nitrate-Rich Vegetables.Foods. 2024 Feb 24;13(5):691. doi: 10.3390/foods13050691. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Health Effects of Dietary Nitrate on Sarcopenia Development: Prospective Evidence from the UK Biobank.Foods. 2024 Dec 27;14(1):43. doi: 10.3390/foods14010043. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39796333 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrate-rich beet juice intake on cardiovascular performance in response to exercise in postmenopausal women with arterial hypertension: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2023 Feb 7;24(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07117-2. Trials. 2023. PMID: 36750904 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Capacity, Nitrite and Nitrate Content in Beetroot-Based Dietary Supplements.Foods. 2023 Feb 27;12(5):1017. doi: 10.3390/foods12051017. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36900534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Health Risks Global Health Risks. [(accessed on 19 August 2018)];Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks. Available online: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/GlobalHealthRisks_re....
-
- World Health Organization Información General Sobre la Hipertensión en el Mundo–OMS. [(accessed on 29 June 2018)];2013 Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/87679/1/WHO_DCO_WHD_2013.2_spa.pdf.
-
- Eckel R.H., Jakicic J.M., Ard J.D., De Jesus J.M., Houston Miller N., Hubbard V.S., Lee I.M., Lichtenstein A.H., Loria C.M., Millen B.E., et al. 2013 AHA/ACC guideline on lifestyle management to reduce cardiovascular risk: A report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014;63:2960–2984. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

