The Parametric Study of Electroosmotically Driven Flow of Power-Law Fluid in a Cylindrical Microcapillary at High Zeta Potential
- PMID: 30400535
- PMCID: PMC6187934
- DOI: 10.3390/mi8120344
The Parametric Study of Electroosmotically Driven Flow of Power-Law Fluid in a Cylindrical Microcapillary at High Zeta Potential
Abstract
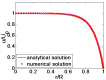
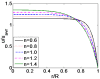
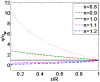
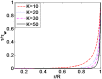
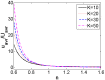
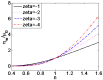
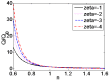
Due to the increasingly wide application of electroosmotic flow in micromachines, this paper investigates the electroosmotic flow of the power-law fluid under high zeta potential in a cylindrical microcapillary for different dimensionless parameters. The electric potential distribution inside a cylindrical microcapillary is presented by the complete Poisson-Boltzmann equation applicable to an arbitrary zeta potential. By solving the Cauchy momentum equation of power-law fluids, the velocity profile, the volumetric flow rate, the average velocity, the shear stress distribution and dynamic viscosity of electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids in a cylindrical microcapillary are studied for different low/high zeta potential, flow behavior index, dimensionless electrokinetic width. The velocity profile gradually changes from parabolic to plug-like shape as the flow behavior index decreases or as the dimensionless electrokinetic width increases. For shear thinning fluids, the viscosity is greater in the center of the microchannel than that near the channel wall, the reverse is true for the shear thickening fluids. Greater volumetric rate and average velocity can be achieved by enhancing the dimensionless electrokinetic width, flow behavior index and zeta potential. It is noted that zeta potential and flow behavior index are important parameters to adjust electroosmotic flow behavior in a cylindrical microcapillary.
Keywords: electroosmotic flow; flow behavior index; high zeta potential; power-law fluids; volumetric flow rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electroosmotic Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluid in Porous Polymer Membrane at High Zeta Potentials.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Nov 27;11(12):1046. doi: 10.3390/mi11121046. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33260968 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear Smoluchowski velocity for electroosmosis of Power-law fluids over a surface with arbitrary zeta potentials.Electrophoresis. 2010 Mar;31(5):973-9. doi: 10.1002/elps.200900564. Electrophoresis. 2010. PMID: 20191559
-
Analysis of electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids in a slit microchannel.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2008 Oct 15;326(2):503-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.06.028. Epub 2008 Jun 19. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2008. PMID: 18656891
-
Interfacial Electric Effects on a Non-Isothermal Electroosmotic Flow in a Microcapillary Tube Filled by Two Immiscible Fluids.Micromachines (Basel). 2017 Jul 27;8(8):232. doi: 10.3390/mi8080232. Micromachines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30400424 Free PMC article.
-
Review on Blood Flow Dynamics in Lab-on-a-Chip Systems: An Engineering Perspective.Chem Bio Eng. 2024 Jan 4;1(1):26-43. doi: 10.1021/cbe.3c00014. eCollection 2024 Feb 22. Chem Bio Eng. 2024. PMID: 39973974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thermally Fully Developed Electroosmotic Flow of Power-Law Nanofluid in a Rectangular Microchannel.Micromachines (Basel). 2019 May 30;10(6):363. doi: 10.3390/mi10060363. Micromachines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31151264 Free PMC article.
-
Electroosmotic Flow of Non-Newtonian Fluid in Porous Polymer Membrane at High Zeta Potentials.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Nov 27;11(12):1046. doi: 10.3390/mi11121046. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33260968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stone H.A., Stroock A.D., Ajdari A. Engineering flows in small devices. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004;36:381–411. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.36.050802.122124. - DOI
-
- Bruus H. Theoretical Microfluidics. Oxford University Press; New York, NY, USA: 2008.
-
- Bayraktar T., Pidugu S.B. Characterization of liquid flows in microfluidic systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 2006;49:815–824. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2005.11.007. - DOI
-
- Nguyen N.T., Wereley S.T. Fundamentals and Applications of Microfluidics. Artech House; Boston, MA, USA: 2006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

