Assessment of Clinical Outcomes after Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy via Esophageal Distensibility Measurements with the Endoluminal Functional Lumen Imaging Probe
- PMID: 30400727
- PMCID: PMC6346997
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl18233
Assessment of Clinical Outcomes after Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy via Esophageal Distensibility Measurements with the Endoluminal Functional Lumen Imaging Probe
Abstract
Background/aims: Endoluminal functional lumen imaging probe (EndoFLIP) is a modality that enables clinicians to measure volume-controlled distension of the esophagus. This study aimed to assess the utility of EndoFLIP in patients who had achalasia treated with peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). We hypothesized that improvement in the distensibility index (DI) is correlated with the postoperative clinical outcome of POEM.
Methods: Patients who underwent POEM for achalasia at Cha Bundang Medical Center were included. Physiological measurements of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure before and after POEM were assessed using EndoFLIP. Patients' symptoms were recorded using the Eckardt score.
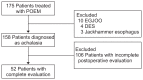
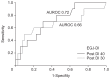
Results: A total of 52 patients with achalasia were included in this study. Patients with a post-POEM DI below 7 (30 or 40 mL) had a significantly higher rate of incomplete response after POEM (p=0.001). Changes in LES pressure or integrated relaxation pressure after POEM were also significantly associated with an incomplete response (p=0.026 and p=0.016, respectively). Multivariate analysis showed that post-POEM DI <7 was the most important predictor of an incomplete response after POEM (p=0.004).
Conclusions: Lower post-POEM DI values were associated with an incomplete post-POEM response. Therefore, post-POEM DI at the esophagogastric junction using EndoFLIP is a useful index for predicting the clinical outcome of POEM in patients with achalasia.
Keywords: Esophageal achalasia; Functional lumen imaging probe; Peroral endoscopic myotomy; Treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Comment in
-
Is EndoFLIP Useful for Predicting Clinical Outcomes after Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy in Patients with Achalasia?Gut Liver. 2019 Jan 15;13(1):3-4. doi: 10.5009/gnl18443. Gut Liver. 2019. PMID: 30665277 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy with EndoFLIP and Double-Endoscope: Novel Techniques for Achalasia in Pediatric Population.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2018 Mar;28(3):343-347. doi: 10.1089/lap.2017.0268. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2018. PMID: 29215957
-
Utility of Intraprocedural Luminal Diameter and Distensibility Measurements During the Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Procedure.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov-Dec 01;58(10):970-974. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001960. Epub 2024 Jan 15. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38227843
-
Intraoperative measurement of esophagogastric junction cross-sectional area by impedance planimetry correlates with clinical outcomes of peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia: a multicenter study.Surg Endosc. 2016 Jul;30(7):2886-94. doi: 10.1007/s00464-015-4574-2. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26487227
-
FLIP use in achalasia: comparing POEM and Heller myotomy outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Surg Endosc. 2025 Jul;39(7):4060-4075. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11776-4. Epub 2025 May 21. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40399616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy in Geriatric Patients with Achalasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Dig Dis. 2022;40(1):106-114. doi: 10.1159/000516024. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Dig Dis. 2022. PMID: 33752208
Cited by
-
Factors associated with peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis.Surg Endosc. 2024 Jul;38(7):3503-3519. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-10862-3. Epub 2024 May 23. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38782829
-
Diagnosis and Management of Esophagogastric Junction Outflow Obstruction.Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2020 Mar;16(3):131-138. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2020. PMID: 34035712 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative distensibility measurement in POEM for achalasia: impact on patient outcome and associations with other outcome variables at 1-year follow-up.Surg Endosc. 2023 Dec;37(12):9283-9290. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10494-z. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37880446 Free PMC article.
-
Devices for esophageal function testing.VideoGIE. 2021 Oct 22;7(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.vgie.2021.08.012. eCollection 2022 Jan. VideoGIE. 2021. PMID: 35059533 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Experience with Endoscopic Pyloromyotomy, with Description and Video of Technique.J Gastrointest Surg. 2019 Aug;23(8):1706-1710. doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04237-6. Epub 2019 May 6. J Gastrointest Surg. 2019. PMID: 31062275
References
-
- Boeckxstaens GE, Annese V, des Varannes SB, et al. Pneumatic dilation versus laparoscopic Heller’s myotomy for idiopathic achalasia. N Engl J Med. 364:1807–1816. 201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

