Periostin involved in the activated hepatic stellate cells-induced progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after sublethal heat treatment: its role and potential for therapeutic inhibition
- PMID: 30400797
- PMCID: PMC6219107
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1676-3
Periostin involved in the activated hepatic stellate cells-induced progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after sublethal heat treatment: its role and potential for therapeutic inhibition
Abstract
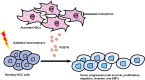
Background: Incomplete thermal ablation may induce invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we investigated whether activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) would accelerate the progression of residual HCC after sublethal heat treatment, and thus sought to identify the potential targets.
Methods: Hepatocellular carcinoma cells were exposed to sublethal heat treatment and then cultured with the conditioned medium from activated HSCs (HSC-CM). The cell proliferation, migration, invasion and parameters of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) were analyzed. In vivo tumor progression of heat-treated residual HCC cells inoculated with activated HSCs was studied in nude mice.
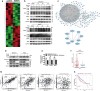
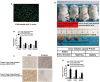
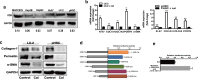
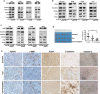
Results: HSC-CM significantly enhanced the proliferation, motility, invasion, prominent EMT activation and decreased apoptosis of heat-exposed residual HCC cells. These increased malignant phenotypes were markedly attenuated by neutralizing periostin (POSTN) in HSC-CM. Furthermore, exogenous POSTN administration exerted the similar effects of HSC-CM on heat-treated residual HCC cells. POSTN induced the prominent activation of p52Shc and ERK1/2 via integrin β1 in heat-exposed residual HCC cells. Vitamin D analog calcipotriol blocked POSTN secretion from activated HSCs. Calcipotriol plus cisplatin significantly suppressed the activated HSCs-enhanced tumor progression of heat-treated residual HCC cells via the inhibited POSTN expression and the increased apoptosis.
Conclusions: Activated HSCs promote the tumor progression of heat-treated residual HCC through the release of POSTN, which could be inhibited by calcipotriol. Calcipotriol plus cisplatin could be used to thwart the accelerated progression of residual HCC after suboptimal heat treatment.
Keywords: Calcipotriol; Hepatic stellate cells; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Periostin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activated hepatic stellate cells secrete periostin to induce stem cell-like phenotype of residual hepatocellular carcinoma cells after heat treatment.Sci Rep. 2017 May 19;7(1):2164. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01177-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28526827 Free PMC article.
-
Activated hepatic stellate cells promote progression of post-heat residual hepatocellular carcinoma from autophagic survival to proliferation.Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):253-263. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1558459. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019. PMID: 30701994
-
Extracellular matrix collagen I promotes the tumor progression of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after heat treatment.BMC Cancer. 2018 Sep 18;18(1):901. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4820-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30227844 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic modulators of hepatic stellate cells for hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2020 Sep 15;147(6):1519-1527. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32899. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32010970 Review.
-
Hepatic stellate cells and extracellular matrix in hepatocellular carcinoma: more complicated than ever.Liver Int. 2014 Jul;34(6):834-43. doi: 10.1111/liv.12465. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 24397349 Review.
Cited by
-
Norepinephrine-stimulated HSCs secrete sFRP1 to promote HCC progression following chronic stress via augmentation of a Wnt16B/β-catenin positive feedback loop.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Apr 15;39(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01568-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32293507 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Insufficient Radiofrequency Ablation.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Apr 26;9:343-355. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S358539. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 35502292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiofrequency ablation: mechanisms and clinical applications.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 2;5(10):e746. doi: 10.1002/mco2.746. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39359691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation: Current status of research.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 22;12:1032746. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1032746. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36483051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Perspectives on the Mechanism of Recurrence After Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Mini-Review.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 23;12:895678. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.895678. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36081558 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

