Investigate the mechanisms of Chinese medicine Fuzhengkangai towards EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinomas by network pharmacology
- PMID: 30400936
- PMCID: PMC6218988
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2347-x
Investigate the mechanisms of Chinese medicine Fuzhengkangai towards EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinomas by network pharmacology
Abstract
Background: Chinese traditional herbal medicine Fuzhengkangai (FZKA) formulation combination with gefitinib can overcome drug resistance and improve the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients. However, the pharmacological and molecular mechanisms underlying the active ingredients, potential targets, and overcome drug resistance of the drug are still unclear. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the molecular mechanism of FZKA.
Methods: A systems pharmacology and bioinformatics-based approach was employed to investigate the molecular pathogenesis of EGFR-TKI resistance with clinically effective herb formula. The differential gene expressions between EGFR-TKI sensitive and resistance cell lines were calculated and used to find overlap from targets as core targets. The prognosis of core targets was validated from the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) database by Cox regression. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment is applied to analysis core targets for revealing mechanism in biology.
Results: The results showed that 35 active compounds of FZKA can interact with eight core targets proteins (ADRB2, BCL2, CDKN1A, HTR2C, KCNMA1, PLA2G4A, PRKCA and LYZ). The risk score of them were associated with overall survival and relapse free time (HR = 6.604, 95% CI: 2.314-18.850; HR = 5.132, 95% CI: 1.531-17.220). The pathway enrichment suggested that they involved in EGFR-TKI resistance and non-small cell lung cancer pathways, which directly affect EGFR-TKI resistance. The molecular docking showed that licochalcone a and beta-sitosterol can closely bind two targets (BCL2 and PRKCA) that involved in EGFR-TKI resistance pathway.
Conclusions: This study provided a workflow for understanding mechanism of CHM for against drug resistance.
Keywords: Fuzhengkangai formula; Herbal medicines; Molecular docking; Systems pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




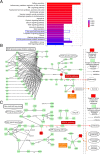

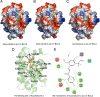
Similar articles
-
A real-world study and network pharmacology analysis of EGFR-TKIs combined with ZLJT to delay drug resistance in advanced lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Nov 21;23(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04213-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37990309 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of "Hedyotis Diffusae Herba-Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma" in treatment of lung adenocarcinoma based on network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Dec;46(23):6261-6270. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210913.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34951253 Chinese.
-
Mechanism of Fuzheng Kang'ai Formula Regulating Tumor Microenvironment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Chin J Integr Med. 2022 May;28(5):425-433. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-3451-1. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Chin J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 34546538
-
Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):593. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020593. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A Review of progresses in research on delayed resistance to EGFR-TKI by Traditional Chinese medicine via inhibiting cancer stem cells properties].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jan;41(1):77-82. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39799429 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Association between Chinese Medicine Therapy and Survival Outcomes in Postoperative Patients with NSCLC: A Multicenter, Prospective, Cohort Study.Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Nov;25(11):812-819. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3168-6. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31471834 Clinical Trial.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of TRP Channel-Related Genes for Estimating the Immune Microenvironment, Prognosis, and Therapeutic Effect in Patients With Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 4;10:820870. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.820870. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35309940 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analysis to Identify a Redox-Related Prognostic Signature for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 21;2021:6648093. doi: 10.1155/2021/6648093. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33968297 Free PMC article.
-
SFI Enhances Therapeutic Efficiency of Gefitinib: An Insight into Reversal of Resistance to Targeted Therapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;11(2):334-344. doi: 10.7150/jca.32989. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31897229 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology Approach for Medicinal Plants: Review and Assessment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 4;15(5):572. doi: 10.3390/ph15050572. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631398 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morosibilot D, Audigiervalette C, Merle P, Quoix E, Souquet PJ, Barlesi F, Chouaid C, Molinier O, Bennouna J, Lavolé A. Non-small cell lung cancer recurrence following surgery and perioperative chemotherapy: comparison of two chemotherapy regimens (IFCT-0702: a randomized phase 3 final results study) Lung Cancer. 2015;89(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.05.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu Y, Chen G, Feng J, Liu X, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(8):710–711. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

