Liver iron sensing and body iron homeostasis
- PMID: 30401708
- PMCID: PMC6318427
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2018-06-815894
Liver iron sensing and body iron homeostasis
Abstract
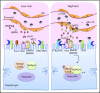
The liver orchestrates systemic iron balance by producing and secreting hepcidin. Known as the iron hormone, hepcidin induces degradation of the iron exporter ferroportin to control iron entry into the bloodstream from dietary sources, iron recycling macrophages, and body stores. Under physiologic conditions, hepcidin production is reduced by iron deficiency and erythropoietic drive to increase the iron supply when needed to support red blood cell production and other essential functions. Conversely, hepcidin production is induced by iron loading and inflammation to prevent the toxicity of iron excess and limit its availability to pathogens. The inability to appropriately regulate hepcidin production in response to these physiologic cues underlies genetic disorders of iron overload and deficiency, including hereditary hemochromatosis and iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia. Moreover, excess hepcidin suppression in the setting of ineffective erythropoiesis contributes to iron-loading anemias such as β-thalassemia, whereas excess hepcidin induction contributes to iron-restricted erythropoiesis and anemia in chronic inflammatory diseases. These diseases have provided key insights into understanding the mechanisms by which the liver senses plasma and tissue iron levels, the iron demand of erythrocyte precursors, and the presence of potential pathogens and, importantly, how these various signals are integrated to appropriately regulate hepcidin production. This review will focus on recent insights into how the liver senses body iron levels and coordinates this with other signals to regulate hepcidin production and systemic iron homeostasis.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.L.B. has ownership interest in Ferrumax Pharmaceuticals and has received consulting fees from Keryx Biopharmaceuticals and Disc Medicine. C.-Y.W. declares no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Fleming MD, Trenor CC III, Su MA, et al. Microcytic anaemia mice have a mutation in Nramp2, a candidate iron transporter gene. Nat Genet. 1997;16(4):383-386. - PubMed
-
- Gunshin H, Mackenzie B, Berger UV, et al. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature. 1997;388(6641):482-488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

