Directed Supramolecular Organization of N-BAR Proteins through Regulation of H0 Membrane Immersion Depth
- PMID: 30401832
- PMCID: PMC6219572
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34273-2
Directed Supramolecular Organization of N-BAR Proteins through Regulation of H0 Membrane Immersion Depth
Abstract
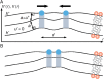
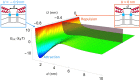
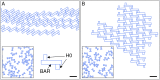
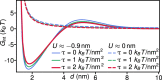
Many membrane remodeling events rely on the ability of curvature-generating N-BAR membrane proteins to organize into distinctive supramolecular configurations. Experiments have revealed a conformational switch in N-BAR proteins resulting in vesicular or tubular membrane shapes, with shallow membrane immersion of the H0 amphipathic helices of N-BAR proteins on vesicles but deep H0 immersion on tubes. We develop here a minimal elastic model of the local thinning of the lipid bilayer resulting from H0 immersion. Our model predicts that the observed conformational switch in N-BAR proteins produces a corresponding switch in the bilayer-mediated N-BAR interactions due to the H0 helices. In agreement with experiments, we find that bilayer-mediated H0 interactions oppose N-BAR multimerization for the shallow H0 membrane immersion depths measured on vesicles, but promote self-assembly of supramolecular N-BAR chains for the increased H0 membrane immersion depths measured on tubes. Finally, we consider the possibility that bilayer-mediated H0 interactions might contribute to the concerted structural reorganization of N-BAR proteins suggested by experiments. Our results indicate that the membrane immersion depth of amphipathic protein helices may provide a general molecular control parameter for membrane organization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

