Palm Fruit Bioactives modulate human astrocyte activity in vitro altering the cytokine secretome reducing levels of TNFα, RANTES and IP-10
- PMID: 30401897
- PMCID: PMC6219577
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34763-3
Palm Fruit Bioactives modulate human astrocyte activity in vitro altering the cytokine secretome reducing levels of TNFα, RANTES and IP-10
Abstract
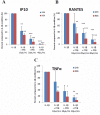
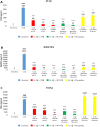
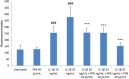
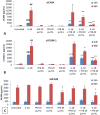
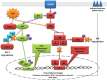
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, are becoming more prevalent and an increasing burden on society. Neurodegenerative diseases often arise in the milieu of neuro-inflammation of the brain. Reactive astrocytes are key regulators in the development of neuro-inflammation. This study describes the effects of Palm Fruit Bioactives (PFB) on the behavior of human astrocytes which have been activated by IL-1β. When activated, the astrocytes proliferate, release numerous cytokines/chemokines including TNFα, RANTES (CCL5), IP-10 (CXCL10), generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), and express specific cell surface biomarkers such as the Intercellular Adhesion Molecule (ICAM), Vascular Cellular Adhesion Molecule (VCAM) and the Neuronal Cellular Adhesion Molecule (NCAM). Interleukin 1-beta (IL-1β) causes activation of human astrocytes with marked upregulation of pro-inflammatory genes. We show significant inhibition of these pro-inflammatory processes when IL-1β-activated astrocytes are exposed to PFB. PFB causes a dose-dependent and time-dependent reduction in specific cytokines: TNFα, RANTES, and IP-10. We also show that PFB significantly reduces ROS production by IL-1β-activated astrocytes. Furthermore, PFB also reduces the expression of ICAM and VCAM, both in activated and naïve human astrocytes in vitro. Since reactive astrocytes play an essential role in the neuroinflammatory state preceding neurodegenerative diseases, this study suggests that PFB may have a potential role in their prevention and/or treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Several of the authors have an equity interest in Phenolaeis, a nutraceutical company incorporated in Malaysia, which has not yet gone into production nor do any of the authors receive any royalties or profits from this entity.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

