Effect of carbamazepine on tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons innervating to the dura
- PMID: 30402025
- PMCID: PMC6205941
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.6.649
Effect of carbamazepine on tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons innervating to the dura
Abstract
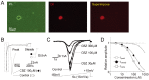
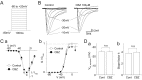
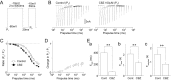
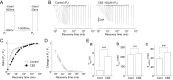
Migraine is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent and disabling severe headaches. Although several anticonvulsant drugs that block voltage-dependent Na+ channels are widely used for migraine, far less is known about the therapeutic actions of carbamazepine on migraine. In the present study, therefore, we characterized the effects of carbamazepine on tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) Na+ channels in acutely isolated rat dural afferent neurons, which were identified by the fluorescent dye DiI. The TTX-R Na+ currents were measured in medium-sized DiIpositive neurons using the whole-cell patch clamp technique in the voltage-clamp mode. While carbamazepine had little effect on the peak amplitude of transient Na+ currents, it strongly inhibited steady-state currents of transient as well as persistent Na+ currents in a concentration-dependent manner. Carbamazepine had only minor effects on the voltage-activation relationship, the voltage-inactivation relationship, and the use-dependent inhibition of TTX-R Na+ channels. However, carbamazepine changed the inactivation kinetics of TTX-R Na+ channels, significantly accelerating the development of inactivation and delaying the recovery from inactivation. In the current-clamp mode, carbamazepine decreased the number of action potentials without changing the action potential threshold. Given that the sensitization of dural afferent neurons by inflammatory mediators triggers acute migraine headaches and that inflammatory mediators potentiate TTX-R Na+ currents, the present results suggest that carbamazepine may be useful for the treatment of migraine headaches.
Keywords: Carbamazepine; Dural afferent neurons; Migraine; Patch clamp; Sodium channel; Tetrodotoxin-resistant.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels by amitriptyline in dural afferent neurons.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 5;838:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30194938
-
Propranolol modulation of tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels in dural afferent neurons.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 5;910:174449. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174449. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34454925
-
Menthol preferentially inhibits persistent Na + current mediated by Na V 1.8 in small-sized dural afferent neurons of rats.Neuroreport. 2025 Aug 6;36(12):687-693. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002189. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Neuroreport. 2025. PMID: 40575871
-
Pregnenolone sulfate potentiates tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ channels to increase the excitability of dural afferent neurons in rats.J Headache Pain. 2025 Feb 25;26(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-01968-7. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40000932 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ currents and inflammatory hyperalgesia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jul 6;96(14):7645-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.14.7645. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10393874 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trigeminal neuralgia: An overview from pathophysiology to pharmacological treatments.Mol Pain. 2020 Jan-Dec;16:1744806920901890. doi: 10.1177/1744806920901890. Mol Pain. 2020. PMID: 31908187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actions of the antiseizure drug carbamazepine in the thalamic reticular nucleus: Potential mechanism of aggravating absence seizures.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 5;122(31):e2500644122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2500644122. Epub 2025 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40743388
References
-
- Goadsby PJ. Recent advances in understanding migraine mechanisms, molecules and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 2007;13:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Diener HC, Dodick DW, Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Olesen J, Silberstein SD. Chronic migraine--classification, characteristics and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012;8:162–171. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari MD. The economic burden of migraine to society. Pharmacoeconomics. 1998;13:667–676. - PubMed
-
- Michel P, Dartigues JF, Lindoulsi A, Henry P. Loss of productivity and quality of life in migraine sufferers among French workers: results from the GAZEL cohort. Headache. 1997;37:71–78. - PubMed
-
- Evers S, Afra J, Frese A, Goadsby PJ, Linde M, May A, Sándor PS. EFNS guideline on the drug treatment of migraine--revised report of an EFNS task force. Eur J Neurol. 2009;16:968–981. - PubMed

