Cerebellar Theta-Burst Stimulation Impairs Memory Consolidation in Eyeblink Classical Conditioning
- PMID: 30402087
- PMCID: PMC6198564
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6856475
Cerebellar Theta-Burst Stimulation Impairs Memory Consolidation in Eyeblink Classical Conditioning
Abstract
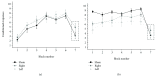
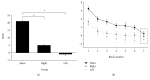
Associative learning of sensorimotor contingences, as it occurs in eyeblink classical conditioning (EBCC), is known to involve the cerebellum, but its mechanism remains controversial. EBCC involves a sequence of learning processes which are thought to occur in the cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei. Recently, the extinction phase of EBCC has been shown to be modulated after one week by cerebellar continuous theta-burst stimulation (cTBS). Here, we asked whether cerebellar cTBS could affect retention and reacquisition of conditioned responses (CRs) tested immediately after conditioning. We also investigated a possible lateralized cerebellar control of EBCC by applying cTBS on both the right and left cerebellar hemispheres. Both right and left cerebellar cTBSs induced a statistically significant impairment in retention and new acquisition of conditioned responses (CRs), the disruption effect being marginally more effective when the left cerebellar hemisphere was stimulated. These data support a model in which cTBS impairs retention and reacquisition of CR in the cerebellum, possibly by interfering with the transfer of memory to the deep cerebellar nuclei.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

