Diverse Expression of IL-32 in Diffuse and Intestinal Types of Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 30402092
- PMCID: PMC6193340
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6578273
Diverse Expression of IL-32 in Diffuse and Intestinal Types of Gastric Cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Gastric cancer (GC) represents one of the most common cancers worldwide, frequently diagnosed at advanced stages with poor prognosis, indicating on need for new diagnostic and prognostic markers. The aim of the study was to determine the expression of IL-32, proinflammatory and angiogenic mediators, in patients with diffuse and intestinal gastric cancer and the relationship with clinicopathological aspects.
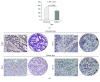
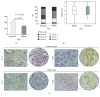
Material and methods: The tissue samples of diffuse and intestinal types of tumor of 70 patients with gastric cancer were analyzed. Expression of IL-32, VEGF, IL-17, and CD31 was measured by immunohistochemistry.
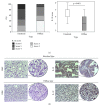
Results: IL-32 expression was significantly lower in tissue samples from patients with diffuse type of gastric cancer that is also a severe and more progressive form (TNM stages III and IV, poor histological differentiation, and higher nuclear grade III). Expression of IL-17 was also decreased in patients with diffuse type of gastric cancer. Microvascular density was diminished in diffuse type of gastric cancer.
Conclusions: Downregulated expression of IL-32 in tumor tissue of patients with diffuse type of gastric cancer may implicate on its role in limiting ongoing proinflammatory and proangiogenic processes. This emphasizes on unrecognized role of IL-32 in biology of diffuse type of gastric cancer.
Figures
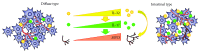
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

