Association between Serum Copeptin and Stroke in Rural Areas of Northern China: A Matched Case-Control Study
- PMID: 30402171
- PMCID: PMC6193346
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9316162
Association between Serum Copeptin and Stroke in Rural Areas of Northern China: A Matched Case-Control Study
Abstract
Background: Copeptin has been implicated as an effective prognostic biomarker of stroke outcome; however, few studies have investigated whether copeptin could be used as an etiological factor for stroke or not. The aim of our study was to evaluate the association of serum copeptin with stroke.
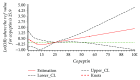
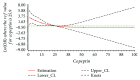
Methods: In total, 238 participants including 119 cases (87 ischemic stroke and 32 hemorrhagic stroke) and 119 controls were included in this 1 : 1 matched case-control study. Conditional multivariate logistic regression was conducted to assess the Odds Ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI); restricted cubic spline in logistic regression model was used to evaluate the dose-response association between serum copeptin and total stroke, ischemic stroke, and hemorrhagic stroke.
Results: The median serum copeptin was 20.90 pmol/L, 20.90 pmol/L, 6.53 pmol/L, and 8.42 pmol/L for total stroke, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, and healthy subjects, respectively. The corresponding ORs (95% CIs) for the highest compared with the lowest quartile were 1.23 (0.62-2.44) for total stroke, 4.01 (1.47-10.96) for ischemic stroke, and 0.13 (0.22-0.69) for hemorrhagic stroke. No nonlinear dose-response relationship was found between serum copeptin and total stroke (P nonlinear = 0.278), ischemic stroke (P nonlinear = 0.362), and hemorrhagic stroke (P nonlinear = 0.314). Compared with the reference copeptin level, a significantly increasing trend was found between serum copeptin and ischemic stroke (P overall = 0.002), and a decreasing trend was found between serum copeptin and hemorrhagic stroke (P overall = 0.007).
Conclusions: Elevated serum copeptin levels were positively associated with ischemic stroke and adversely associated with hemorrhagic stroke. Additional prospective studies with larger sample size are needed to confirm the present findings.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Copeptin Kinetics in Acute Ischemic Stroke May Differ According to Revascularization Strategies: Pilot Data.Stroke. 2019 Dec;50(12):3632-3635. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025433. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Stroke. 2019. PMID: 31630623
-
Serum Copeptin Predicts Severity and Recurrent Stroke in Ischemic Stroke Patients.Neurotox Res. 2017 Oct;32(3):420-425. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9754-5. Epub 2017 May 30. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 28555260
-
Plasma copeptin and functional outcome in patients with ischemic stroke and type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Complications. 2016 Nov-Dec;30(8):1532-1536. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.07.030. Epub 2016 Jul 30. J Diabetes Complications. 2016. PMID: 27554438
-
Copeptin as a biomarker for prediction of prognosis of acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: a meta-analysis.Hypertens Res. 2017 May;40(5):465-471. doi: 10.1038/hr.2016.165. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Hypertens Res. 2017. PMID: 27904159 Review.
-
Higher Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 Levels and the Risk of Stroke and Its Subtypes: Evidence From a Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Nov;27(11):3076-3083. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.06.040. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 30077605 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating Serum Copeptin as a Promising Biomarker for Predicting Acute Ischaemic Stroke Severity: A Hospital-Based Study on Strokes.Cureus. 2024 Jul 2;16(7):e63700. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63700. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38957516 Free PMC article.
-
Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 1;26(11):5328. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115328. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Big Data-Enabled Analysis of DRGs-Based Payment on Stroke Patients in Jiaozuo, China.J Healthc Eng. 2020 Dec 2;2020:6690019. doi: 10.1155/2020/6690019. eCollection 2020. J Healthc Eng. 2020. PMID: 33343852 Free PMC article.
-
Association between PPARG genetic polymorphisms and ischemic stroke risk in a northern Chinese Han population: a case-control study.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Nov;14(11):1986-1993. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.259621. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 31290457 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic value of copeptin in patients with acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cardiol J. 2022;29(4):610-618. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2022.0045. Epub 2022 May 27. Cardiol J. 2022. PMID: 35621091 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

