Understanding psoriasis: Role of miRNAs
- PMID: 30402223
- PMCID: PMC6200992
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2018.1146
Understanding psoriasis: Role of miRNAs
Abstract
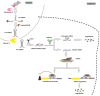
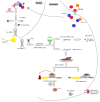
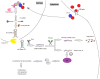
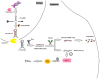
Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory skin disease, with a multifactorial etiology and important immunologic, genetic and environmental components. Psoriasis vulgaris represents its most common form, with a variable prevalence across the globe. Although its pathogenesis remains to be fully elucidated, a lack of balance in the epigenetic network has been shown to trigger certain elements of this disease, possibly altering its outcome. MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNA molecules involved in RNA-silencing and the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression, which also appear to mediate the immune dysfunction in psoriasis. Although microRNA research is a new field in dermatology and psoriasis, there is rapidly accumulating evidence for its major contribution in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory conditions, including psoriasis and other dermatological disorders. Furthermore, circulating miRNAs identified in patients' blood samples have been identified as promising biomarkers of diagnosis, prognosis or treatment response. Extended investigations in this field are required, as until now, the exact involvement of miRNAs in psoriasis have remained to be entirely elucidated. This short review highlights a number of the roles of miRNAs found in different stages of psoriasis.
Keywords: immune system; keratinocytes; microRNA; psoriasis.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
