Multiple Regression Analysis Reveals MicroRNA Regulatory Networks in Oryza sativa under Drought Stress
- PMID: 30402456
- PMCID: PMC6196795
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9395261
Multiple Regression Analysis Reveals MicroRNA Regulatory Networks in Oryza sativa under Drought Stress
Abstract
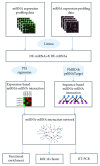
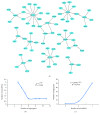
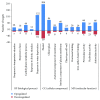
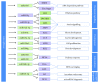
Drought is a major abiotic stress that reduces rice development and yield. miRNAs (microRNAs) are known to mediate posttranscriptional regulation under drought stress. Although the importance of individual miRNAs has been established, the crosstalks between miRNAs and mRNAs remain unearthed. Here we performed microarray analysis of miRNAs and matched mRNA expression profiles of drought-treated rice cultivar Nipponbare. Drought-responsive miRNA-mRNA regulations were identified by a combination of a partial least square (PLS) regression approach and sequence-based target prediction. A drought-induced network with 13 miRNAs and 58 target mRNAs was constructed, and four miRNA coregulatory modules were revealed. Functional analysis suggested that drought-response miRNA targets are enriched in hormone signaling, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, and antioxidant defense. 13 candidate miRNAs and target genes were validated by RT-qPCR, hierarchical clustering, and ROC analysis. Two target genes (DWARF-3 and P0651G05.2) of miRNA coregulatory modules were further verified by RLM-5' RACE. Together, our integrative study of miRNA-mRNA interaction provided attractive candidates that will help elucidate the drought-response mechanisms in Oryza sativa.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of four functionally important microRNA families with contrasting differential expression profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible rice leaf at vegetative stage.BMC Genomics. 2015 Sep 15;16(1):692. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1851-3. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26369665 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic regulatory networks mediated by microRNAs and transcription factors under drought, heat and salt stresses in Oryza Sativa spp.Gene. 2015 Jan 25;555(2):127-39. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.10.054. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25445270
-
Transcriptome profiling of drought responsive noncoding RNAs and their target genes in rice.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 8;17:563. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2997-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27501838 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress.J Exp Bot. 2015 Apr;66(7):1749-61. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv013. Epub 2015 Feb 19. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25697792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of microRNAs in the mediation of drought stress response in plants.J Exp Bot. 2013 Aug;64(11):3077-86. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert164. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 23814278 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of hub genes and key pathways in arsenic-treated rice (Oryza sativa L.) based on 9 topological analysis methods of CytoHubba.Environ Health Prev Med. 2024;29:41. doi: 10.1265/ehpm.24-00095. Environ Health Prev Med. 2024. PMID: 39111872 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Exogenous Nitric Oxide-Responsive miRNAs from Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under Drought Stress by High-Throughput Sequencing.Genes (Basel). 2019 Dec 26;11(1):30. doi: 10.3390/genes11010030. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31888061 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Heat-Response Mechanisms of MicroRNAs Based on Microarray Data of Rice Post-meiosis Panicle.Int J Genomics. 2020 Sep 17;2020:7582612. doi: 10.1155/2020/7582612. eCollection 2020. Int J Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33015150 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Modifications of Hormonal Signaling Pathways in Plant Drought Response and Tolerance for Sustainable Food Security.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 28;25(15):8229. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158229. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Drought Stress Responsive microRNAs in Tibetan Wild Barley.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 17;21(8):2795. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082795. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32316632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ala U., Karreth F. A., Bosia C., et al. Integrated transcriptional and competitive endogenous RNA networks are cross-regulated in permissive molecular environments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013;110(18):7154–7159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222509110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

