Intermittent Hypoxia Enhances THP-1 Monocyte Adhesion and Chemotaxis and Promotes M1 Macrophage Polarization via RAGE
- PMID: 30402462
- PMCID: PMC6196992
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1650456
Intermittent Hypoxia Enhances THP-1 Monocyte Adhesion and Chemotaxis and Promotes M1 Macrophage Polarization via RAGE
Abstract
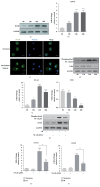
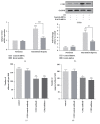
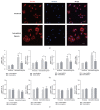
Intermittent hypoxia (IH) that resulted from obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has been found to be a risk factor of coronary artery disease. IH and the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) expression are known to activate monocyte/macrophage and associated with atherosclerosis development, while their effects on monocyte adhesion, chemotaxis to the endothelium, and macrophage polarization remain unknown. In the present study, RAGE in THP-1 monocytes was inhibited by shRNA lentiviral particles, followed by exposure to IH. Cell adhesion assay, transwell migration assay, and macrophage polarization assays were performed to study the effects of IH and RAGE. The mRNA and protein expression levels were investigated by RT/real-time PCR and western blot analysis, respectively. We found that IH increased RAGE expression and activated NF-кB signalling in THP-1 monocytes. The results also revealed that IH enhanced the MCP-1-mediated THP-1 monocyte adhesion and chemotaxis and promoted macrophage polarization toward a proinflammatory phenotype, which was mediated by RAGE activity. Additionally, inhibition of chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2) suppressed the IH-induced monocyte adhesion and chemotaxis. These results demonstrated a potential role of monocyte adhesion, chemotaxis, and macrophage polarization in the development cardiovascular diseases induced by IH and identified that RAGE could be a promising therapeutic target to prevent atherosclerosis in patients with OSA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased C-C chemokine receptor 2 gene expression in monocytes of severe obstructive sleep apnea patients and under intermittent hypoxia.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 20;9(11):e113304. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113304. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25411969 Free PMC article.
-
Monocytic C-C chemokine receptor 5 expression increases in in vitro intermittent hypoxia condition and in severe obstructive sleep apnea patients.Sleep Breath. 2019 Dec;23(4):1177-1186. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01797-4. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Sleep Breath. 2019. PMID: 30778913 Free PMC article.
-
Cilostazol reduces MCP-1-induced chemotaxis and adhesion of THP-1 monocytes by inhibiting CCR2 gene expression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jul 29;411(2):402-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.163. Epub 2011 Jul 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21756880
-
Intermittent hypoxia and activation of inflammatory molecular pathways in OSAS.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2008 Oct;114(4):261-6. doi: 10.1080/13813450802307337. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18946786 Review.
-
Adhesion-dependent modulation of macrophage K+ channels.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;674:81-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6066-5_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20549942 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Metabolic Reprogramming to Improve Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 24;22(19):10268. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910268. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of Circulating CD14/CD16 Monocyte Subsets in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Patients upon Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 9;10(8):1925. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081925. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009474 Free PMC article.
-
New insights from integrated bioinformatics analysis: the role of circadian rhythm disruption and immune infiltration in obstructive sleep apnea disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 15;14:1273114. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273114. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38169659 Free PMC article.
-
Daily Eicosapentaenoic Acid Infusion in IUGR Fetal Lambs Reduced Systemic Inflammation, Increased Muscle ADRβ2 Content, and Improved Myoblast Function and Muscle Growth.Metabolites. 2024 Jun 18;14(6):340. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060340. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38921474 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Atherosclerosis by Toll-Like Receptor 4 Induced by Serum Amyloid 1: A Systematic In Vitro Study.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 15;2022:4887593. doi: 10.1155/2022/4887593. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36158875 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

