Optimal effective-site concentration of remifentanil for sedation during plate removal of maxilla
- PMID: 30402549
- PMCID: PMC6218391
- DOI: 10.17245/jdapm.2018.18.5.295
Optimal effective-site concentration of remifentanil for sedation during plate removal of maxilla
Abstract
Background: Removal of the plate following Le Fort I osteotomy and BSSO (bilateral sagittal split osteotomy) is a common procedure. However, patients who undergo plate removal experience intense pain and discomfort. This study investigated the half-maximal effective concentration (Ce50 ) of remifentanil in the prevention of plate removal pain under sedation using dexmedetomidine.
Methods: The study evaluated 18 patients, between 18 and 35 years of age, scheduled for elective surgery. Remifentanil infusion was initiated after sedation using dexmedetomidine, and started at a dose of 1.5 ng/mL on the first patient via target-controlled infusion (TCI). Patients received a loading dose of 1.0 µg/kg dexmedetomidine over 10 min, followed by a maintenance dose of 0.7 µg/kg/h. When the surgeon removed the plate, the patient Modified Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation (MOAA/S) score was observed.
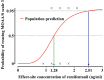
Results: The Ce of remifentanil ranged from 0.9 to 2.1 ng/mL for the patients evaluated. The estimated effect-site concentrations of remifentanil associated with a 50% and 95% probability of reaching MOAA/S score of 3 were 1.28 and 2.51 ng/mL, respectively.
Conclusions: Plate removal of maxilla can be successfully performed without any pain or adverse effects by using the optimal remifentanil effect-site concentration (Ce50 , 1.28 ng/mL; Ce95 , 2.51 ng/mL) combined with sedation using dexmedetomidine.
Keywords: Conscious Sedation, Dexmedetomidine; Plate Removal; Remifentanil.
Conflict of interest statement
NOTEThere are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimal effect-site concentration of remifentanil when combined with dexmedetomidine in patients undergoing cystoscopy.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014 Jan;66(1):39-43. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.1.39. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014. PMID: 24567812 Free PMC article.
-
Target-controlled infusion of dexmedetomidine effect-site concentration for sedation in patients undergoing spinal anaesthesia.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020 Apr;45(2):347-353. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13085. Epub 2019 Dec 5. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020. PMID: 31802541 Clinical Trial.
-
Target-controlled infusion of remimazolam effect-site concentration for total intravenous anesthesia in patients undergoing minimal invasive surgeries.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 17;11:1364357. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1364357. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38695029 Free PMC article.
-
[Study of comparing dexmedetomidine and remifentanil for conscious sedation during radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Feb 27;98(8):576-580. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.08.004. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29534384 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Optimal effect-site concentration of remifentanil to prevent hemodynamic changes during nasotracheal intubation using a video laryngoscope.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020 Aug;20(4):195-202. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2020.20.4.195. Epub 2020 Aug 27. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020. PMID: 32934985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matthew IR, Frame JW. Policy of consultant oral and maxillofacial surgeons towards removal of miniplate components after jaw fracture fixation: pilot study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;37:110–112. - PubMed
-
- Falter B, Schepers S, Vrielinck L, Lambrichts I, Politis C. Plate removal following orthognathic surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112:737–743. - PubMed
-
- Hall JE, Uhrich TD, Barney JA, Arain SR, Ebert TJ. Sedative, amnestic, and analgesic properties of small-dose dexmedetomidine infusions. Anesth Analg. 2000;90:699–705. - PubMed
-
- Ebert TJ, Hall JE, Barney JA, Uhrich TD, Colinco MD. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:382–394. - PubMed
-
- Herr DL, Sum-Ping ST, England M. ICU sedation after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: dexmedetomidine-based versus propofol-based sedation regimens. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2003;17:576–584. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

