Suspicious Lesion Segmentation on Brain, Mammograms and Breast MR Images Using New Optimized Spatial Feature Based Super-Pixel Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
- PMID: 30402671
- PMCID: PMC6456642
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-018-0149-9
Suspicious Lesion Segmentation on Brain, Mammograms and Breast MR Images Using New Optimized Spatial Feature Based Super-Pixel Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
Abstract
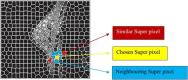
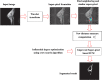
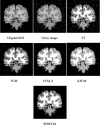
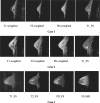
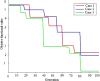
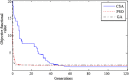
Suspicious lesion or organ segmentation is a challenging task to be solved in most of the medical image analyses, medical diagnoses and computer diagnosis systems. Nevertheless, various image segmentation methods were proposed in the previous studies with varying success levels. But, the image segmentation problems such as lack of versatility, low robustness, high complexity and low accuracy in up-to-date image segmentation practices still remain unsolved. Fuzzy c-means clustering (FCM) methods are very well suited for segmenting the regions. The noise-free images are effectively segmented using the traditional FCM method. However, the segmentation result generated is highly sensitive to noise due to the negligence of spatial information. To solve this issue, super-pixel-based FCM (SPOFCM) is implemented in this paper, in which the influence of spatially neighbouring and similar super-pixels is incorporated. Also, a crow search algorithm is adopted for optimizing the influential degree; thereby, the segmentation performance is improved. In clinical applications, the SPOFCM feasibility is verified using the multi-spectral MRIs, mammograms and actual single spectrum on performing tumour segmentation tests for SPOFCM. Ultimately, the competitive, renowned segmentation techniques such as k-means, entropy thresholding (ET), FCM, FCM with spatial constraints (FCM_S) and kernel FCM (KFCM) are used to compare the results of proposed SPOFCM. Experimental results on multi-spectral MRIs and actual single-spectrum mammograms indicate that the proposed algorithm can provide a better performance for suspicious lesion or organ segmentation in computer-assisted clinical applications.
Keywords: Breast MR images; Clinical application; Fuzzy C-means; Mammograms; Spatial; Super-pixel.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A segmentation of brain MRI images utilizing intensity and contextual information by Markov random field.Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2017 Dec;22(sup1):200-211. doi: 10.1080/24699322.2017.1389398. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2017. PMID: 29072503
-
Robust image segmentation using FCM with spatial constraints based on new kernel-induced distance measure.IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern. 2004 Aug;34(4):1907-16. doi: 10.1109/tsmcb.2004.831165. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern. 2004. PMID: 15462455
-
Improved Fuzzy C-Means based Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) initialization and outlier rejection with level set methods for MR brain image segmentation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2015 Nov;122(2):266-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2015. PMID: 26299609
-
A New Optimized Thresholding Method Using Ant Colony Algorithm for MR Brain Image Segmentation.J Digit Imaging. 2019 Feb;32(1):162-174. doi: 10.1007/s10278-018-0111-x. J Digit Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30091112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancements in Fuzzy C-means Based Techniques for Brain MRI Segmentation.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(8):917-930. doi: 10.2174/1573405616666210104111218. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33397241 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of MRI images based on Spatial Fuzzy Clustering Algorithm guided by Neuroendoscopy in the treatment of Tumors in the Saddle Region.Pak J Med Sci. 2021;37(6):1600-1604. doi: 10.12669/pjms.37.6-WIT.4850. Pak J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34712290 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Risk Assessment: A Review on Mammography-Based Approaches.J Imaging. 2021 Jun 12;7(6):98. doi: 10.3390/jimaging7060098. J Imaging. 2021. PMID: 39080886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm-Based ARM-Linux-Embedded System Combined with Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Progression Prediction of Brain Tumors.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Mar 15;2022:4224749. doi: 10.1155/2022/4224749. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35341006 Free PMC article.
-
A Bottom-Up Review of Image Analysis Methods for Suspicious Region Detection in Mammograms.J Imaging. 2021 Sep 18;7(9):190. doi: 10.3390/jimaging7090190. J Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34564116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang ZM, Soh YC, Song Q, Sim K. Adaptive spatial information-theoretic clustering for image segmentation. Pattern Recogn. 2009;42(9):2029–2044. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.01.023. - DOI
-
- Tou JT, Gonzalez RC. Pattern recognition. Reading: Addison-Wesley; 1974.
-
- Modha DS, Spangler WS. Feature weighting in k-means clustering. Mach Learn. 2003;52(3):217–237. doi: 10.1023/A:1024016609528. - DOI
-
- Bezdek JC, Ehrlich R, Full W. FCM: the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput Geosci. 1984;10(2):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0098-3004(84)90020-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

