Amyloid beta soluble forms and plasminogen activation system in Alzheimer's disease: Consequences on extracellular maturation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 30403004
- PMCID: PMC6488905
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13082
Amyloid beta soluble forms and plasminogen activation system in Alzheimer's disease: Consequences on extracellular maturation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and therapeutic implications
Abstract
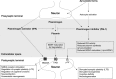
Soluble oligomeric forms of amyloid beta (Aβ) play an important role in causing the cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease (AD) by targeting and disrupting synaptic pathways. Thus, the present research is directed toward identifying the neuronal pathways targeted by soluble forms and, accordingly, develops alternative therapeutic strategies. The neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is synthesized as a precursor (pro-BDNF) which is cleaved extracellularly by plasmin to release the mature form. The conversion from pro-BDNF to BDNF is an important process that regulates neuronal activity and memory processes. Plasmin-dependent maturation of BDNF in the brain is regulated by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), the natural inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA). Therefore, tPA/PAI-1 system represents an important regulator of extracellular BDNF/pro-BDNF ratio. In this review, we summarize the data on the components of the plasminogen activation system and on BDNF in AD. Moreover, we will hypothesize a possible pathogenic mechanism caused by soluble Aβ forms based on the effects on tPA/PAI-1 system and on the consequence of an altered conversion from pro-BDNF to the mature BDNF in the brain of AD patients. Translation into clinic may include a better characterization of the disease stage and future direction on therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid beta; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; tissue-type plasminogen activator.
© 2018 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of BDNF cleavage by plasminogen-activator inhibitor-1 contributes to Alzheimer's neuropathology and cognitive deficits.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Apr;1863(4):991-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.01.023. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28132883
-
Impacts of aging and amyloid-β deposition on plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res. 2015 Feb 9;1597:159-67. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.042. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25454795
-
Neuropep-1 ameliorates learning and memory deficits in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model, increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the brain, and causes reduction of amyloid beta plaques.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 May;35(5):990-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.091. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24268884
-
The probable role of tissue plasminogen activator/neuroserpin axis in Alzheimer's disease: a new perspective.Acta Neurol Belg. 2024 Apr;124(2):377-388. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02403-x. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Acta Neurol Belg. 2024. PMID: 37917293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of CREB and BDNF in neurobiology and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 15;257:118020. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118020. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32603820 Review.
Cited by
-
A Narrative Review on Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Its (Patho)Physiological Role: To Target or Not to Target?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 8;22(5):2721. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052721. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity during late pregnancy by modulating apoptotic pathways and BDNF receptor expression.Exp Brain Res. 2025 Mar 21;243(4):96. doi: 10.1007/s00221-025-07050-7. Exp Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40116959
-
Blood protein profiles related to preterm birth and retinopathy of prematurity.Pediatr Res. 2022 Mar;91(4):937-946. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01528-0. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 33895781 Free PMC article.
-
Minoxidil Regulates Aging-Like Phenotypes in Rat Cortical Astrocytes In Vitro.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023 Jan 1;31(1):116-126. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.144. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 36535699 Free PMC article.
-
Immune markers are associated with cognitive performance in a multiethnic cohort: The Northern Manhattan Study.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Oct;97:186-192. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.07.011. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 34320382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:329‐344. - PubMed
-
- Cavallucci V, D'Amelio M, Cecconi F. Aβ toxicity in Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012;45:366‐378. - PubMed
-
- Price JL, Morris JC. Tangles and plaques in nondemented aging and “preclinical” Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol. 1999;45:358‐368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

