Water-soluble cranberry extract inhibits Vibrio cholerae biofilm formation possibly through modulating the second messenger 3', 5' - Cyclic diguanylate level
- PMID: 30403745
- PMCID: PMC6221352
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207056
Water-soluble cranberry extract inhibits Vibrio cholerae biofilm formation possibly through modulating the second messenger 3', 5' - Cyclic diguanylate level
Abstract
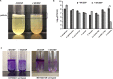
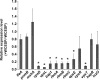
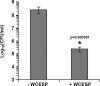
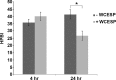
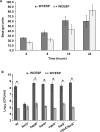
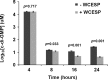
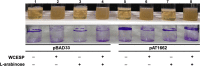
Quorum sensing (QS) and nucleotide-based second messengers are vital signaling systems that regulate bacterial physiology in response to changing environments. Disrupting bacterial signal transduction is a promising direction to combat infectious diseases, and QS and the second messengers are undoubtedly potential targets. In Vibrio cholerae, both QS and the second messenger 3', 5'-cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP) play a central role in controlling motility, motile-to-sessile life transition, and virulence. In this study, we found that water-soluble extract from the North American cranberry could significantly inhibit V. cholerae biofilm formation during the development/maturation stage by reducing the biofilm matrix production and secretion. The anti-biofilm effect by water-soluble cranberry extract was possibly through modulating the intracellular c-di-GMP level and was independent of QS and the QS master regulator HapR. Our results suggest an opportunity to explore more functional foods to fight stubborn infections through interference with the bacterial signaling systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu J, Mekalanos JJ. Quorum sensing-dependent biofilms enhance colonization in Vibrio cholerae. Dev Cell. 2003;5(4):647–56. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

