Advances in Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Food and Water Analysis
- PMID: 30404261
- PMCID: PMC6189793
- DOI: 10.3390/mi7050086
Advances in Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Food and Water Analysis
Abstract
Food and water contamination cause safety and health concerns to both animals and humans. Conventional methods for monitoring food and water contamination are often laborious and require highly skilled technicians to perform the measurements, making the quest for developing simpler and cost-effective techniques for rapid monitoring incessant. Since the pioneering works of Whitesides' group from 2007, interest has been strong in the development and application of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) for food and water analysis, which allow easy, rapid and cost-effective point-of-need screening of the targets. This paper reviews recently reported μPADs that incorporate different detection methods such as colorimetric, electrochemical, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, and electrochemiluminescence techniques for food and water analysis.
Keywords: food analysis; point-of-need; water analysis; μPADs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

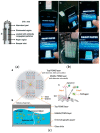
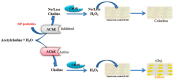

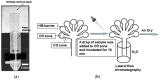

References
-
- International Agency for Research in Cancer (IARC) IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans: Some Food Additives, Feed Additives and Naturally Occurring Substances. Volume 31. World Health Organization; Lyon, France: 1983. 2-(2-Furyl)-3-(5-nitro-2-fyryl)acrylamide (AF-2) p. 41.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

