Quantification of Vortex Generation Due to Non-Equilibrium Electrokinetics at the Micro/Nanochannel Interface: Particle Tracking Velocimetry
- PMID: 30404299
- PMCID: PMC6190468
- DOI: 10.3390/mi7070127
Quantification of Vortex Generation Due to Non-Equilibrium Electrokinetics at the Micro/Nanochannel Interface: Particle Tracking Velocimetry
Abstract
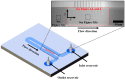
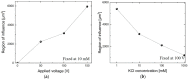
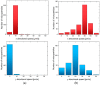
We describe a quantitative study of vortex generation due to non-equilibrium electrokinetics near a micro/nanochannel interface. The microfluidic device is comprised of a microchannel with a set of nanochannels. These perm-selective nanochannels induce flow instability and thereby produce strong vortex generation. We performed tracking visualization of fluorescent microparticles to obtain velocity fields. Particle tracking enables the calculation of an averaged velocity field and the velocity fluctuations. We characterized the effect of applied voltages and electrolyte concentrations on vortex formation. The experimental results show that an increasing voltage or decreasing concentration results in a larger vortex region and a strong velocity fluctuation. We calculate the normalized velocity fluctuation-whose meaning is comparable to turbulent intensity-and we found that it is as high as 0.12. This value is indicative of very efficient mixing, albeit with a small Reynolds number.
Keywords: microparticle; nanochannel; particle tracking velocimetry; vortex generation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantification of Vortex Generation Due to Non-Equilibrium Electrokinetics at the Micro/Nanochannel Interface: Spectral Analysis.Micromachines (Basel). 2016 Jun 27;7(7):109. doi: 10.3390/mi7070109. Micromachines (Basel). 2016. PMID: 30404283 Free PMC article.
-
Non-equilibrium electrokinetic micromixer with 3D nanochannel networks.Lab Chip. 2015 Apr 21;15(8):1794-8. doi: 10.1039/c4lc01435a. Lab Chip. 2015. PMID: 25710479
-
Junction flow inside and around three-row cylindrical group on rigid flat surface.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 24;8(12):e12595. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12595. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36643326 Free PMC article.
-
Particle tracking techniques for electrokinetic microchannel flows.Anal Chem. 2002 Aug 1;74(15):3704-13. doi: 10.1021/ac011243s. Anal Chem. 2002. PMID: 12175157
-
Micro-Scale Particle Tracking: From Conventional to Data-Driven Methods.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 May 8;15(5):629. doi: 10.3390/mi15050629. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrodialytic Processes: Market Overview, Membrane Phenomena, Recent Developments and Sustainable Strategies.Membranes (Basel). 2020 Sep 2;10(9):221. doi: 10.3390/membranes10090221. Membranes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32887428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification of Vortex Generation Due to Non-Equilibrium Electrokinetics at the Micro/Nanochannel Interface: Spectral Analysis.Micromachines (Basel). 2016 Jun 27;7(7):109. doi: 10.3390/mi7070109. Micromachines (Basel). 2016. PMID: 30404283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eijkel J.C., van den Berg A. Nanofluidics: What is it and what can we expect from it? Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2005;1:249–267. doi: 10.1007/s10404-004-0012-9. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

