The relationship between plasma renin activity and serum lipid profiles in patients with primary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 30404585
- PMCID: PMC6240969
- DOI: 10.1177/1470320318810022
The relationship between plasma renin activity and serum lipid profiles in patients with primary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Introduction:: The aim of the study was to evaluate clinical and biochemical differences between patients with low-renin and high-renin primary arterial hypertension (AH), mainly in reference to serum lipids, and to identify factors determining lipid concentrations.
Materials and methods:: In untreated patients with AH stage 1 we measured plasma renin activity (PRA) and subdivided the group into low-renin (PRA < 0.65 ng/mL/h) and high-renin (PRA ⩾ 0.65 ng/mL/h) AH. We compared office and 24-h ambulatory blood pressure, serum aldosterone, lipids and selected biochemical parameters between subgroups. Factors determining lipid concentration in both subgroups were assessed in regression analysis.
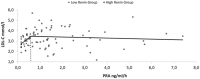
Results:: Patients with high-renin hypertension ( N = 58) were characterized by higher heart rate ( p = 0.04), lower serum sodium ( p < 0.01) and aldosterone-to-renin ratio ( p < 0.01), and significantly higher serum aldosterone ( p = 0.03), albumin ( p < 0.01), total protein ( p < 0.01), total cholesterol ( p = 0.01) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ( p = 0.04) than low-renin subjects ( N = 39). In univariate linear regression, only PRA in the low-renin group was in a positive relationship with LDL-C ( R2 = 0.15, β = 1.53 and p = 0.013); this association remained significant after adjustment for age, sex, and serum albumin and aldosterone concentrations.
Conclusions:: Higher serum levels of total and LDL-C characterized high-renin subjects, but the association between LDL-C level and PRA existed only in low-renin primary AH.
Keywords: Arterial hypertension; aldosterone; aldosterone-to-renin ratio; plasma renin activity; serum lipids.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum uric acid is not independently associated with plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone in hypertensive adults.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 Apr;27(4):350-359. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28274727
-
Low plasma renin activity and high aldosterone/renin ratio are associated with untreated isolated systolic hypertension.Blood Press. 2012 Oct;21(5):320-5. doi: 10.3109/08037051.2012.686167. Epub 2012 May 16. Blood Press. 2012. PMID: 22587638
-
[Differences of blood plasma renin activity, angiotensin II and aldosterone levels in essential or secondary hypertension].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;51(4):294-8. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781950 Chinese.
-
Aldosterone Levels, Aortic Stiffness, and Wave Reflection in Essential Hypertensive Patients.Am J Hypertens. 2015 Jul;28(7):852-7. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpu244. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Am J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25542624
-
Plasma renin activity, serum aldosterone concentration and selected organ damage indices in essential arterial hypertension.Arch Med Sci. 2018 Feb 7;17(1):9-18. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2018.73333. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 33488850 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of dyslipidemia and oxidative stress on vasoactive mediators in patients with renal dysfunction.Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Dec;51(12):2235-2242. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02319-7. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31641998 Review.
-
Evaluation of Active Renin Concentration in A Cohort of Adolescents with Primary Hypertension.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 13;19(10):5960. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19105960. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35627493 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a) and the risk of type I cardiorenal syndrome in patients with coronary artery disease: A retrospective clinical study.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 Dec 6;56:101568. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101568. eCollection 2025 Feb. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 39720339 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-Angiotensin System in Liver Metabolism: Gender Differences and Role of Incretins.Metabolites. 2022 May 3;12(5):411. doi: 10.3390/metabo12050411. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35629915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Laragh JH. Laragh’s lesson in renin system pathophysiology for treating hypertension and its fatal cardiovascular consequences. New York: Elsevier, 2002.
-
- Pizoń T, Rajzer M, Kameczura T. The role of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in etiology and pathogenesis of arterial hypertension and its systemic complications - what remains from Laragh and Alderman idea? Arterial Hypertens 2011; 15: 371–382.
-
- Ferrario CM, Strawn WB. Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and proinflammatory mediators in cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 2006; 98: 121–128. - PubMed
-
- Funder JW, Reincke M. Aldosterone: A cardiovascular risk factor? Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1802: 1188–1192. - PubMed
-
- Marney AM, Brown NJ. Aldosterone and end-organ damage. Clin Sci 2007; 113: 267–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

