Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Leader Protease Cleaves G3BP1 and G3BP2 and Inhibits Stress Granule Formation
- PMID: 30404792
- PMCID: PMC6321903
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00922-18
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Leader Protease Cleaves G3BP1 and G3BP2 and Inhibits Stress Granule Formation
Abstract
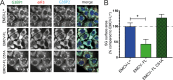
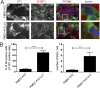
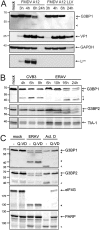
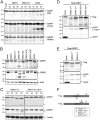
Like other viruses, the picornavirus foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV; genus Aphthovirus), one of the most notorious pathogens in the global livestock industry, needs to navigate antiviral host responses to establish an infection. There is substantial insight into how FMDV suppresses the type I interferon (IFN) response, but it is largely unknown whether and how FMDV modulates the integrated stress response. Here, we show that the stress response is suppressed during FMDV infection. Using a chimeric recombinant encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV), in which we functionally replaced the endogenous stress response antagonist by FMDV leader protease (Lpro) or 3Cpro, we demonstrate an essential role for Lpro in suppressing stress granule (SG) formation. Consistently, infection with a recombinant FMDV lacking Lpro resulted in SG formation. Additionally, we show that Lpro cleaves the known SG scaffold proteins G3BP1 and G3BP2 but not TIA-1. We demonstrate that the closely related equine rhinitis A virus (ERAV) Lpro also cleaves G3BP1 and G3BP2 and also suppresses SG formation, indicating that these abilities are conserved among aphthoviruses. Neither FMDV nor ERAV Lpro interfered with phosphorylation of RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) or eIF2α, indicating that Lpro does not affect SG formation by inhibiting the PKR-triggered signaling cascade. Taken together, our data suggest that aphthoviruses actively target scaffolding proteins G3BP1 and G3BP2 and antagonize SG formation to modulate the integrated stress response.IMPORTANCE The picornavirus foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) is a notorious animal pathogen that puts a major economic burden on the global livestock industry. Outbreaks have significant consequences for animal health and product safety. Like many other viruses, FMDV must manipulate antiviral host responses to establish infection. Upon infection, viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is detected, which results in the activation of the RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR)-mediated stress response, leading to a stop in cellular and viral translation and the formation of stress granules (SG), which are thought to have antiviral properties. Here, we show that FMDV can suppress SG formation via its leader protease (Lpro). Simultaneously, we observed that Lpro can cleave the SG scaffolding proteins G3BP1 and G3BP2. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of the antiviral host response evasion strategies of FMDV may help to develop countermeasures to control FMDV infections in the future.
Keywords: Aphthovirus; FMDV; G3BP1; G3BP2; SGs; Stress granules.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Essential Role of Enterovirus 2A Protease in Counteracting Stress Granule Formation and the Induction of Type I Interferon.J Virol. 2019 May 1;93(10):e00222-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00222-19. Print 2019 May 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30867299 Free PMC article.
-
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus 3A Protein Causes Upregulation of Autophagy-Related Protein LRRC25 To Inhibit the G3BP1-Mediated RIG-Like Helicase-Signaling Pathway.J Virol. 2020 Mar 31;94(8):e02086-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02086-19. Print 2020 Mar 31. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31996428 Free PMC article.
-
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Counteracts on Internal Ribosome Entry Site Suppression by G3BP1 and Inhibits G3BP1-Mediated Stress Granule Assembly via Post-Translational Mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2018 May 25;9:1142. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01142. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29887867 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Targeting the Host Antiviral Response.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 13;7:252. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00252. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28660175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional roles of leader protein of foot-and-mouth disease viruses in suppressing host antiviral responses.Vet Res. 2015 Oct 28;46:127. doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0273-1. Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 26511922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-Viral and Anti-Viral Roles of the RNA-Binding Protein G3BP1.Viruses. 2023 Feb 6;15(2):449. doi: 10.3390/v15020449. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of G3BP1 in bovine parainfluenza virus type 3 (BPIV3)-inhibition of stress granules formation and viral replication.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 16;15:1358036. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1358036. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38690262 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia facilitates EV71 replication: Insights into miR-206-mediated regulation of G3BP2 promoting EV71 IRES activity.Theranostics. 2024 Apr 22;14(7):2706-2718. doi: 10.7150/thno.93883. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38773966 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology of stress granules: An emerging link to diseases (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Apr;49(4):44. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5099. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35137915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Lb Protease Cleaves Intracellular Transcription Factors STAT1 and STAT2 to Antagonize IFN-β-Induced Signaling.J Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;210(3):283-296. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101042. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36548461 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

