Segmentation of the Proximal Femur from MR Images using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
- PMID: 30405145
- PMCID: PMC6220200
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34817-6
Segmentation of the Proximal Femur from MR Images using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
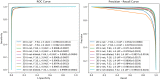
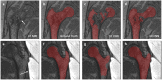
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been proposed as a complimentary method to measure bone quality and assess fracture risk. However, manual segmentation of MR images of bone is time-consuming, limiting the use of MRI measurements in the clinical practice. The purpose of this paper is to present an automatic proximal femur segmentation method that is based on deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs). This study had institutional review board approval and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. A dataset of volumetric structural MR images of the proximal femur from 86 subjects were manually-segmented by an expert. We performed experiments by training two different CNN architectures with multiple number of initial feature maps, layers and dilation rates, and tested their segmentation performance against the gold standard of manual segmentations using four-fold cross-validation. Automatic segmentation of the proximal femur using CNNs achieved a high dice similarity score of 0.95 ± 0.02 with precision = 0.95 ± 0.02, and recall = 0.95 ± 0.03. The high segmentation accuracy provided by CNNs has the potential to help bring the use of structural MRI measurements of bone quality into clinical practice for management of osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
G.C. has a pending patent application (# 62/593,626) filed by the University of Iowa. G.C. shares the invention with Punam Saha. Specific aspects of this manuscript were not covered in the patent application. The other authors do not have conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Genant Harry K., Engelke Klaus, Fuerst Thomas, Glüer Claus-C., Grampp Stephan, Harris Steven T., Jergas Michael, Lang Thomas, Lu Ying, Majumdar Sharmila, Mathur Ashwini, Takada Masa. Noninvasive assessment of bone mineral and structure: State of the art. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2009;11(6):707–730. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650110602. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Okazaki Narihiro, Chiba Ko, Taguchi Kenji, Nango Nobuhito, Kubota Shogo, Ito Masako, Osaki Makoto. Trabecular microfractures in the femoral head with osteoporosis: Analysis of microcallus formations by synchrotron radiation micro CT. Bone. 2014;64:82–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2014.03.039. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

