Viability of Lactobacillus plantarum on Fresh-Cut Chitosan and Alginate-Coated Apple and Melon Pieces
- PMID: 30405587
- PMCID: PMC6205977
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02538
Viability of Lactobacillus plantarum on Fresh-Cut Chitosan and Alginate-Coated Apple and Melon Pieces
Abstract
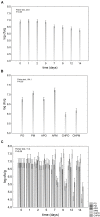
There is an increasing trend toward foods with probiotics; the awareness of healthy diet and wellbeing is the leading cause of this increase. As a result, food producers and stakeholders require new probiotic products. The increased incidence of lactose intolerance and the new lifestyles (vegan and vegetarian styles) have led to a renewed interest in non-dairy probiotic carriers. The use of biopolymeric matrices to develop active food packaging carrying probiotics has been studied and proposed as an alternative method to design new solutions. The main topic of this paper was the design of fresh-cut fruits (apples and melons) as carriers for a promising Lactobacillus plantarum; fruit pieces were coated with either alginate or chitosan. Apple (Granny Smith) and melon pieces (Cucumis melo, var. Cantalupensis) were preliminary treated with an anti-browning solution (citric and ascorbic acids). Then, fruit pieces were dipped in a solution containing L. plantarum c19 (9 log cfu/ml) and coated with alginate or chitosan. Samples without probiotic and/or coatings were used as controls. All samples were stored at 4°C for 14 days under air or modified atmosphere (65% N2, 30% CO2, and 5% O2); the following analyses were done: pH, color, O2, and CO2 in the head space, microbiology (mesophilic bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, yeasts, and molds). The most important results can be summarized as follows: (a) Alginate coating showed better performances than chitosan-coating, as it did not affect the viability of L. plantarum. (b) The inoculation of probiotics in the controls negatively affected the color, but the coating was able to counteract this effect. This paper supports the combination of edible coatings and probiotic as a promising way to design new fruit-based functional foods; further investigations are required to study the effect of this combination on the sensory scores.
Keywords: edible coating; fresh-cut; fruit pieces; probiotic; shelf life.
Figures




References
-
- Allende A., Tomás-Barberán F. A., Gil M. I. (2006). Minimal processing for healthy traditional foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 17 513–519. 10.1016/j.tifs.2006.04.005 - DOI
-
- Bevilacqua A., Altieri C., Corbo M. R., Sinigaglia M., Ouoba L. I. I. (2010). Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Italian Bella di Cerignola table olives: selection of potential multifunctional starter cultures. J. Food Sci. 75 M536–M544. 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01793.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

