The Combination Therapy of Dietary Galacto-Oligosaccharides With Budesonide Reduces Pulmonary Th2 Driving Mediators and Mast Cell Degranulation in a Murine Model of House Dust Mite Induced Asthma
- PMID: 30405619
- PMCID: PMC6207001
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02419
The Combination Therapy of Dietary Galacto-Oligosaccharides With Budesonide Reduces Pulmonary Th2 Driving Mediators and Mast Cell Degranulation in a Murine Model of House Dust Mite Induced Asthma
Abstract
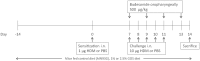
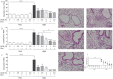
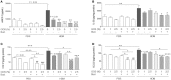
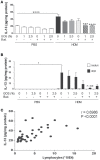
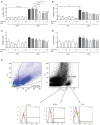
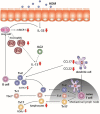
Background: Dietary non-digestible galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) suppress allergic responses in mice sensitized and challenged with house dust mite (HDM). Budesonide is the standard therapy for allergic asthma in humans but is not always completely effective. Aim: To compare the efficacy of budesonide or different doses of GOS alone or with a combination therapy of budesonide and GOS on HDM-allergic responses in mice. Methods:BALB/c mice were sensitized and challenged with HDM, while fed a control diet or a diet supplemented with 1 or 2.5 w/w% GOS, and either or not oropharyngeally instilled with budesonide. Systemic and local inflammatory markers, such as mucosal mast cell protease-1 (mMCP-1) in serum, pulmonary CCL17, CCL22, and IL-33 concentrations and inflammatory cell influx in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were determined. Results: Budesonide or GOS alone suppressed the number of eosinophils in the BALF of HDM allergic mice whereas budesonide either or not combined with GOS lowered both eosinophil and lymphocyte numbers in the BALF of HDM-allergic mice. Both 1 w/w% and 2.5 w/w% GOS and/or budesonide suppressed serum mMCP-1 concentrations. However, budesonide nor GOS alone was capable of reducing Th2 driving chemokines CCL17, CCL22 and IL-33 protein levels in supernatants of lung homogenates of HDM allergic mice, whereas the combination therapy did. Moreover, IL-13 concentrations were only significantly suppressed in mice treated with budesonide while fed GOS. A similar tendency was observed for the frequency of GATA3+CD4+ Th2 and CD4+RORγt+ Th17 cells in the lungs of the allergic mice. Conclusion: Dietary intervention using GOS may be a novel way to further improve the efficacy of anti-inflammatory drug therapy in allergic asthma by lowering Th2 driving mediators and mast cell degranulation.
Keywords: allergy; asthma; budesonide; galacto-oligosaccharides; house dust mite.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary galacto-oligosaccharides prevent airway eosinophilia and hyperresponsiveness in a murine house dust mite-induced asthma model.Respir Res. 2015 Feb 7;16(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0171-0. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 25849971 Free PMC article.
-
The development of allergic inflammation in a murine house dust mite asthma model is suppressed by synbiotic mixtures of non-digestible oligosaccharides and Bifidobacterium breve M-16V.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Apr;55(3):1141-51. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0928-8. Epub 2015 May 24. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26003185 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T Cell Depletion Abolishes the Protective Effect of Dietary Galacto-Oligosaccharides on Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in House Dust Mite-Induced Asthma in Mice.J Nutr. 2015 Apr 1;146(4):831-837. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.224402. J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26962188
-
Efficacy and safety of SQ house dust mite (HDM) SLIT-tablet treatment of HDM allergic asthma.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016 Aug;12(8):805-15. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2016.1200467. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27322777 Review.
-
Modeling responses to respiratory house dust mite exposure.Contrib Microbiol. 2007;14:42-67. doi: 10.1159/000107054. Contrib Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17684332 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-Based Dietary Fibers and Polysaccharides as Modulators of Gut Microbiota in Intestinal and Lung Inflammation: Current State and Challenges.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 26;15(15):3321. doi: 10.3390/nu15153321. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUL-151 Decreases Airway Neutrophilia as a Prophylactic and Therapeutic Treatment in Mice after Cigarette Smoke Exposure.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 8;22(9):4991. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094991. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066693 Free PMC article.
-
Crude Turmeric Extract Improves the Suppressive Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on Allergic Inflammation in a Murine Model of House Dust Mite-Induced Asthma.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 4;11:1092. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01092. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582180 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Fibers: Effects, Underlying Mechanisms and Possible Role in Allergic Asthma Management.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 19;13(11):4153. doi: 10.3390/nu13114153. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in intestinal homeostasis and immunity in a cigarette smoke- and LPS-induced murine model for COPD: the lung-gut axis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022 Sep 1;323(3):L266-L280. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00486.2021. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35699290 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

