Pharmacologic Effect of Miao Medicine Illicium simonsii Maxim. on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats
- PMID: 30405736
- PMCID: PMC6201380
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/2398379
Pharmacologic Effect of Miao Medicine Illicium simonsii Maxim. on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats
Abstract
Objectives: To study the pharmacologic effect and mechanism of action of Miao medicine Illicium simonsii Maxim. (ISM) in treating rheumatoid arthritis.
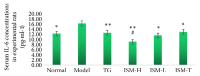
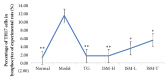
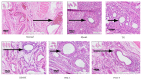
Methods: Sixty rats were randomly divided to six groups: normal control (normal), collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model (model), CIA + tripterygium glycosides (TG), CIA + ISM high dose oral (ISM-H), CIA + ISM low-dose oral (ISM-L), and CIA + ISM topical application (ISM-T). The treatment doses were selected based on published reports and folk medicine practice. The outcome measurements included paw swelling, joint pathology, organ index, blood count, T helper 17 (Th17) cell count, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) level.
Results: Compared to the CIA model group, all treatment groups showed a significant reduction in paw swelling, blood vessel pathology, Th17 cell count, and IL-6 levels (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01). All treatment groups showed alleviated foot swelling and lower total number of white blood cells, and these effects were observed earlier with oral ISM than topical ISM. The effect of ISM was weaker than that of TG. In addition, less organ damage was observed with topical ISM than oral ISM but better than TG.
Conclusions: These results suggest that, by downregulating Th17 cells, ISM inhibits the production of Il-6, thereby alleviating the proliferation of endothelial and rheumatoid-like cells and leukocytosis in CIA rats, ultimately eliminating foot swelling.
Figures
References
-
- Xu C., Wang X., Mu R., et al. Social costs of rheumatoid arthritis in China: a hospital-based cross-sectional study. Arthritis Care & Research. 2014;66(4):523–531. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

