Upregulation of circRNA_0000285 serves as a prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is involved in radiosensitivity
- PMID: 30405788
- PMCID: PMC6202549
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9471
Upregulation of circRNA_0000285 serves as a prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is involved in radiosensitivity
Abstract
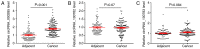
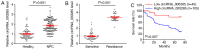
Despite significant medical advancement, nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) remains one of the most difficult types of cancer to detect and treat. Circular RNA (circRNA) signatures may be used as prognostic and predictive factors for cancer. Previous studies indicated that the biological role of circular homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3 (HIPK3) has cancer type-specificity. The HIPK3 gene locus formats three circRNA isoforms: circRNA_100783, circRNA_0000285 and circRNA_100782. However, their roles in NPC remain unknown. In the present study, whether these circRNAs could be used as a biomarker for NPC diagnosis and predicting treatment response was investigated. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed to measure the levels of circRNA_100783, circRNA_0000285 and circRNA_100782 in NPC and adjacent tissues. In addition, the circRNA_0000285 levels were further confirmed in serum samples from patients with NPC and healthy controls. The results demonstrated that circRNA_0000285, but not circRNA_100782 and circRNA_100783, was significantly increased in NPC tissues and serum samples from patients with NPC, compared with adjacent tissues and serum samples from healthy controls, respectively. Furthermore, circRNA_0000285 expression was increased in patients with radioresistant NPC, compared with patients with radiosensitive NPC. Further analysis demonstrated that circRNA_0000285 was significantly associated with tumor size (P<0.001), differentiation (P=0.022), lymph node metastasis (P=0.035), distant metastasis (P=0.022) and Tumor-Node-Metastasis stage (P<0.001). Additionally, univariate and multivariate analyses indicated that circRNA_0000285 may be an independent prognostic factor for the outcome of patients with NPC. The present data indicated that circRNA_0000285 may be a novel biomarker for NPC and is involved in NPC radiosensitivity.
Keywords: biomarker; circRNA_0000285; circular RNA; circular homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; radiosensitivity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CircRNA_000543 knockdown sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to irradiation by targeting miR-9/platelet-derived growth factor receptor B axis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 May 14;512(4):786-792. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.126. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30928094
-
High Expression of hsa_circRNA_001387 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and the Effect on Efficacy of Radiotherapy.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 8;13:3965-3973. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S249202. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32440159 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin resistance-associated circRNA_101237 serves as a prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Apr;19(4):2733-2740. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8526. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32226487 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA Expression Profiles in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Sequence Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 30;10:601. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00601. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32426279 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of phosphorylated Raf kinase inhibitory protein at serine 153 and its predictive effect on the clinical response to radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Radiat Oncol. 2016 Sep 20;11(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0696-5. Radiat Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27647315 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CircLASP1 silence strengthens the therapeutic effects of MK-2206 on nasopharyngeal cancer through upregulating miR-625.Cancer Sci. 2023 May;114(5):2123-2138. doi: 10.1111/cas.15725. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36644819 Free PMC article.
-
CircCTDP1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via a microRNA‑320b/HOXA10/TGFβ2 pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Mar;45(3):836-846. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4467. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31985027 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Underlying Mechanisms of Circular RNAs and Their Application in Clinical Research of Cervical Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 25;12:653051. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.653051. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33841509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Star Circular RNAs In Human Cancer: Progress And Perspectives.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Oct 7;12:8249-8261. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S215390. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31632075 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress of circRNAs in Head and Neck Cancers.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 29;11:616202. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.616202. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33996542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee AW, Poon YF, Foo W, Law SC, Cheung FK, Chan DK, Tung SY, Thaw M, Ho JH. Retrospective analysis of 5037 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during 1976–1985: Overall survival and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;23:261–270. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(92)90740-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
