Low expression of miR-199 in hepatocellular carcinoma contributes to tumor cell hyper-proliferation by negatively suppressing XBP1
- PMID: 30405792
- PMCID: PMC6202493
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9476
Low expression of miR-199 in hepatocellular carcinoma contributes to tumor cell hyper-proliferation by negatively suppressing XBP1
Abstract
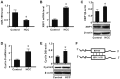
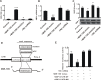
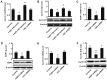
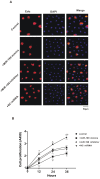
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, and microRNAs (miRs) are considered to serve important functions in the pathogenesis of HCC by regulating the expression of specific target genes. The present study was conducted to investigate the role of miR-199 and its putative target X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) in HCC, as well as of the downstream gene cyclin D. The expression levels of miR-199, XBP1 and cyclin D were detected in clinical HCC specimens. The effect of miR-199 on the regulation of HCC cell proliferation and its underlying mechanism were examined in Hep3B2.1-7 cells, through expression assays and measurement of cell proliferation (via Cell Counting Kit-8, and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine and DAPI double-staining assays) coupled with gain- and lose- of function experiments. The expression of XBP1 and cyclin D was significantly increased in HCC tissues when compared with adjacent non-HCC tissues, while the expression of miR-199 was decreased. Exogenous miR-199 significantly suppressed the expression of XBP1 and cyclin D in Hep3B2.1-7 cells. However, the expression of XBP1 and cyclin D significantly increased on treatment with miR-199 inhibitor. Consistently, Hep3B2.1-7 cells co-transfected with a wild type reporter plasmid [XBP1-3'untranslated region (UTR)-WT] and exogenous miR-199 exhibited lower relative luciferase enzyme activity than cells co-transfected with negative control miRNA and XBP1-3'UTR-WT, while cells co-transfected with mutated plasmid (XBP1-3'UTR-MU) and miR-199 exhibited no change. It was further observed that knockdown of XBP1 by small interfering RNA significantly decreased the expression of cyclin D in Hep3B2.1-7 cells. Additionally, exogenous miR-199 decreased the proliferation of Hep3B2.1-7 cells, which was contrary to the effect of miR-199 inhibitor. In conclusion, it was demonstrated that miR-199 negatively regulated the expression of XBP1 by directly binding to its 3'UTR and that XBP1 impacted cyclin D expression, which was associated with the cell cycle regulation in Hep3B2.1-7 cells. These findings suggested that a miR-199/XBP1/cyclin D axis may serve an important role in the pathogenesis of HCC.
Keywords: X-box binding protein 1; cell proliferation; cyclin D; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver cancer; microRNA-199; microRNAs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[LncRNA HULC promots HCC growth by downregulating miR-29].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019 Sep 23;41(9):659-666. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.09.004. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31550855 Chinese.
-
[The effects of microRNA-7 on proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 23;40(6):406-411. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.06.002. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29936764 Chinese.
-
MicroRNA-101 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma progression through EZH2 downregulation and increased cytostatic drug sensitivity.J Hepatol. 2014 Mar;60(3):590-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.10.028. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24211739
-
Catalpol inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration through regulating miR-22-3p/MTA3 signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma.Exp Mol Pathol. 2019 Aug;109:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104265. Epub 2019 May 27. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31145886
-
HOXA-AS2 Promotes Proliferation and Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the miR-520c-3p/GPC3 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(6):2124-2138. doi: 10.1159/000495056. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30415263
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-587 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Ribosomal Protein SA.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Sep 5;2020:3280530. doi: 10.1155/2020/3280530. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32964027 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Thyroid Hormone-Associated microRNAs Affecting Oxidative Stress in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 21;20(20):5220. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205220. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31640265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Significance of hsa-miR-21-5p, hsa-miR-192-5p, hsa-miR-155-5p, hsa-miR-199a-5p Panel and Ratios in Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Top of Liver Cirrhosis in HCV-Infected Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3157. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043157. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834570 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Low Cytoplasmic Expression of XBP1 and the Likelihood of Surviving Hepatocellular Carcinoma.In Vivo. 2024 May-Jun;38(3):1316-1324. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13571. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38688649 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Processes of Ferroptosis Involved in Pathogenesis of COVID-19 and Core Ferroptoic Genes Related With the Occurrence and Severity of This Disease.Evol Bioinform Online. 2023 Feb 13;19:11769343231153293. doi: 10.1177/11769343231153293. eCollection 2023. Evol Bioinform Online. 2023. PMID: 36820229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Kulathinal RJ, Blain SW, Holcombe RF, Mahajna J, Marino M, Martinez-Chantar ML, Nawroth R, Sanchez-Garcia I, Sharma D, et al. Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015;35:S25–S54. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
