Survival analysis for lung adenosquamous carcinoma patients with brain metastasis
- PMID: 30405840
- PMCID: PMC6216008
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.27441
Survival analysis for lung adenosquamous carcinoma patients with brain metastasis
Abstract
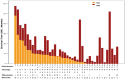
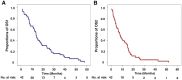
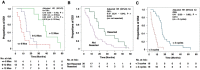
Purpose: We retrospectively collected consecutive survival data of lung adenosquamous cell carcinoma (ASC) patients with brain metastasis (BM) in our institute and discussed the factors related to prognosis of these patients. Patients and Methods: A total of 42 patients diagnosed as lung ASC with BM between July 1, 2008 and December 31, 2010 at the Department of Respiratory Medicine, Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University were retrospectively reviewed. Time to BM (TTB) and overall survival (OS) data were analyzed. OS1 was calculated from the time ASC was diagnosed until the death of a patient. OS2 was defined as the duration from BM was first identified to the death of a patient. 1-year, 2-year and 3-year survival rates were also computed. Univariate and multivariate survival analysis was performed using Kaplan-Meier methods and Cox regression. Results: The median TTB for all patients was 5.7 months [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.8 - 10.6 months]. The median OS1 was 13.8 months (95%CI: 11.2 - 16.4 months). TTB longer than 12 months [adjusted HR: 0.15 (95%CI: 0.05 -0.48 vs. TTB≤ 6 months, P=0.001); 0.22 (95%CI: 0.07- 0.71, vs. TTB 6-12 months, P=0.010) and resection for BM lesions [adjusted hazard ratio (HR): 0.47 (95%CI: 0.24 - 0.94 vs. not resected, P=0.032)] were independent predictors for a longer OS1. The median OS2 was 7.9 months (95%CI: 4.5 - 11.3 months). Treatment cycles more than 3 [adjusted HR: 0.41 (95%CI: 0.20 - 0.83 vs. treatment cycles <3, P=0.013)] was an independent predictor for a longer OS2. Conclusions: This study shows that resection of BM if possible, and standard chemo-radiotherapy in patients with multiple BM lesions is associated with longer overall survival.
Keywords: brain metastasis (BM).; lung adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC); lung cancer; non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC); survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):10–29. - PubMed
-
- Filosso PL, Ruffini E, Asioli S. et al. Adenosquamous lung carcinomas: a histologic subtype with poor prognosis. Lung Cancer. 2011;74:25–9. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu J, Oda M, Hayashi Y. et al. A clinicopathologic study of resected cases of adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung. Chest. 1996;109:989–94. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgibbons PL, Kern WH. Adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung: a clinical and pathologic study of seven cases. Hum Pathol. 1985;16(5):463–6. - PubMed
-
- Ishida T, Kaneko S, Yokoyama H. et al. Adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung. Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical features. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992;97:678–85. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

