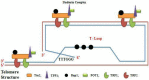
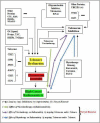
Effect of therapies-mediated modulation of telomere and/or telomerase on cancer cells radiosensitivity
- PMID: 30405890
- PMCID: PMC6201854
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26150
Effect of therapies-mediated modulation of telomere and/or telomerase on cancer cells radiosensitivity
Abstract
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in the world. Many strategies of cancer treatment such as radiotherapy which plays a key role in cancer treatment are developed and used nowadays. However, the side effects post-cancer radiotherapy and cancer radioresistance are two major causes of the limitation of cancer radiotherapy effectiveness in the cancer patients. Moreover, reduction of the limitation of cancer radiotherapy effectiveness by reducing the side effects post-cancer radiotherapy and cancer radioresistance is the aim of several radiotherapy-oncologic teams. Otherwise, Telomere and telomerase are two cells components which play an important role in cancer initiation, cancer progression and cancer therapy resistance such as radiotherapy resistance. For resolving the problems of the limitation of cancer radiotherapy effectiveness especially the cancer radio-resistance problems, the radio-gene-therapy strategy which is the use of gene-therapy via modulation of gene expression combined with radiotherapy was developed and used as a new strategy to treat the patients with cancer. In this review, we summarized the information concerning the implication of telomere and telomerase modulation in cancer radiosensitivity.
Keywords: cancer cells; radiosensitivity; radiotherapy; telomerase; telomere.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No competing interests regarding this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of telomeres in predicting individual radiosensitivity of patients with cancer in the era of personalized radiotherapy.Cancer Treat Rev. 2015 Apr;41(4):354-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015. PMID: 25704912 Review.
-
Effect of modulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators Snail1 and Snail2 on cancer cell radiosensitivity by targeting of the cell cycle, cell apoptosis and cell migration/invasion.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jan;17(1):23-30. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9636. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30655734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere dysfunction is related to the intrinsic radio-resistance of human oral cancer cells.Oral Oncol. 2008 Mar;44(3):261-9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2007.02.010. Epub 2007 May 1. Oral Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17475542
-
Downregulation of high mobility group box 1 modulates telomere homeostasis and increases the radiosensitivity of human breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2015 Mar;46(3):1051-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2793. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25501936
-
Suppression of PinX1 resulted in telomere dysfunction and enhanced radiosensitivity in osteosarcoma cell lines.Neoplasma. 2015;62(6):887-93. doi: 10.4149/neo_2015_108. Neoplasma. 2015. PMID: 26458319
Cited by
-
BIBR1532 combined with radiotherapy induces ferroptosis in NSCLC cells and activates cGAS-STING pathway to promote anti-tumor immunity.J Transl Med. 2024 May 30;22(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05331-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38816831 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear WRAP53 promotes neuronal survival and functional recovery after stroke.Sci Adv. 2020 Oct 7;6(41):eabc5702. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc5702. Print 2020 Oct. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33028529 Free PMC article.
-
Telomeres and Telomere Length: A General Overview.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 28;12(3):558. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030558. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32121056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, Casey DC, Charlson FJ, Chen AZ, Coates MM, Coggeshall M, Dandona L, Dicker DJ, et al. GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1459–544. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sakurai Y, Kajimoto K, Harashima H. Anti-angiogenic nanotherapy via active targeting systems to tumors and adipose tissue vasculature. Biomater Sci. 2015;3:1253–65. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources