Estrogen reinforces barrier formation and protects against tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced barrier dysfunction in oral epithelial cells
- PMID: 30405936
- PMCID: PMC6207799
- DOI: 10.5051/jpis.2018.48.5.284
Estrogen reinforces barrier formation and protects against tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced barrier dysfunction in oral epithelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: Epithelial barrier dysfunction is involved in the pathophysiology of periodontitis and oral lichen planus. Estrogens have been shown to enhance the physical barrier function of intestinal and esophageal epithelia, and we aimed to investigate the effect of estradiol (E2) on the regulation of physical barrier and tight junction (TJ) proteins in human oral epithelial cell monolayers.
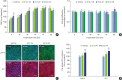
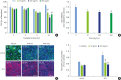
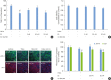
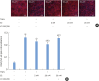
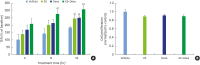
Methods: HOK-16B cell monolayers cultured on transwells were treated with E2, an estrogen receptor (ER) antagonist (ICI 182,780), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), or dexamethasone (Dexa), and the transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) was then measured. Cell proliferation was measured by the cell counting kit (CCK)-8 assay. The levels of TJ proteins and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB were examined by confocal microscopy.
Results: E2 treatment increased the TER and the levels of junctional adhesion molecule (JAM)-A and zonula occludens (ZO)-1 in a dose-dependent manner, without affecting cell proliferation during barrier formation. Treatment of the tight-junctioned cell monolayers with TNFα induced decreases in the TER and the levels of ZO-1 and nuclear translocation of NF-κB. These TNFα-induced changes were inhibited by E2, and this effect was completely reversed by co-treatment with ICI 182,780. Furthermore, E2 and Dexa presented an additive effect on the epithelial barrier function.
Conclusions: E2 reinforces the physical barrier of oral epithelial cells through the nuclear ER-dependent upregulation of TJ proteins. The protective effect of E2 on the TNFα-induced impairment of the epithelial barrier and its additive effect with Dexa suggest its potential use to treat oral inflammatory diseases involving epithelial barrier dysfunction.
Keywords: Epithelial cells; Junctional adhesion molecule A; NF-kappa B; Tight junctions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Turner JR. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:799–809. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

