Dynamic proteomic changes in soft wheat seeds during accelerated ageing
- PMID: 30405971
- PMCID: PMC6216954
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.5874
Dynamic proteomic changes in soft wheat seeds during accelerated ageing
Abstract
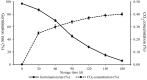
Previous research demonstrated that soft wheat cultivars have better post-harvest storage tolerance than harder cultivars during accelerated ageing. To better understand this phenomenon, a tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteomic analysis of soft wheat seeds was performed at different storage times during accelerated ageing (germination ratios of 97%, 45%, 28%, and 6%). A total of 1,010 proteins were differentially regulated, of which 519 and 491 were up- and downregulated, respectively. Most of the differentially expressed proteins were predicted to be involved in nutrient reservoir, enzyme activity and regulation, energy and metabolism, and response to stimulus functions, consistent with processes occurring in hard wheat during artificial ageing. Notably, defense-associated proteins including wheatwin-2, pathogenesis-related proteins protecting against fungal invasion, and glutathione S-transferase and glutathione synthetase participating in reactive oxygen species (ROS) detoxification, were upregulated compared to levels in hard wheat during accelerated ageing. These upregulated proteins might be responsible for the superior post-harvest storage-tolerance of soft wheat cultivars during accelerated ageing compared with hard wheat. Although accelerated ageing could not fully mimic natural ageing, our findings provided novel dynamic proteomic insight into soft wheat seeds during seed deterioration.
Keywords: Accelerated ageing; Post-harvest storage-tolerance; Proteomics; Soft wheat seeds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative Acetylome Analysis of Soft Wheat Seeds during Artificial Ageing.Foods. 2022 Nov 12;11(22):3611. doi: 10.3390/foods11223611. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36429203 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Wheat Seeds during Artificial Ageing and Priming Using the Isobaric Tandem Mass Tag Labeling.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 15;11(9):e0162851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162851. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27632285 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative physiology and proteomics of two wheat genotypes differing in seed storage tolerance.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018 Sep;130:455-463. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.07.022. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30077921
-
Comparative proteome analysis of embryo and endosperm reveals central differential expression proteins involved in wheat seed germination.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Apr 8;15:97. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0471-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25888100 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome analysis of maize seeds: the effect of artificial ageing.Physiol Plant. 2011 Oct;143(2):126-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2011.01497.x. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Physiol Plant. 2011. PMID: 21707636
Cited by
-
Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Ridge Gourd Seed (Luffa acutangula (L.) Roxb.) during Artificial Aging.ACS Omega. 2024 May 30;9(23):24739-24750. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01270. eCollection 2024 Jun 11. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38882140 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species-induced protein carbonylation promotes deterioration of physiological activity of wheat seeds.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 31;17(3):e0263553. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263553. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35358205 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the proteomic profile of newly harvested corn and metagenomic analysis of the broiler intestinal microbiota.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 9;13(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00656-1. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35135621 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping biochemical and nutritional changes in durum wheat due to spoilage during storage.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 8;9(11):e22139. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22139. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38045167 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Acetylome Analysis of Soft Wheat Seeds during Artificial Ageing.Foods. 2022 Nov 12;11(22):3611. doi: 10.3390/foods11223611. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36429203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calucci L, Capocchi A, Galleschi L, Ghiringhelli S, Pinzino C, Saviozzi F, Zandomeneghi M. Antioxidants, free radicals, storage proteins, puroindolines, and proteolytic activities in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) seeds during accelerated aging. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2004;52:4274–4281. doi: 10.1021/jf0353741. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Galleschi L, Capocchi A, Ghiringhelli S, Saviozzi F, Calucci L, Pinzino C, Zandomeneghi M. Antioxidants, free radicals, storage proteins, and proteolytic activities in wheat (Triticum durum) seeds during accelerated aging. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2002;50:5450–5457. doi: 10.1021/jf0201430. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

