Tumor Volume Reduction After Gemcitabine Plus Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Comparison with Paclitaxel and Cisplatin Regimens
- PMID: 30406770
- PMCID: PMC6237045
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.909736
Tumor Volume Reduction After Gemcitabine Plus Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Comparison with Paclitaxel and Cisplatin Regimens
Abstract
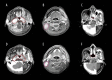
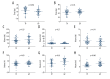
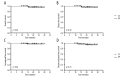
BACKGROUND Gemcitabine plus cisplatin (GP) is a novel regimen of induction chemotherapy (IC) for treating locoregional advanced nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC). This retrospective study aimed to compare the efficacy of GP and TP (paclitaxel plus cisplatin) regimens in tumor volume reduction after IC. MATERIAL AND METHODS Between January 2014 and July 2017, 44 patients with III-IVB stage NPC received GP IC followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy. These patients were matched with 44 patients receiving TP IC according to clinical characteristics. The gross tumor volume of the primary site and positive lymph nodes were delineated by magnetic resonance imaging before and after IC, as well as the nasopharyngeal air cavities. The changes in tumor volume and nasopharyngeal air cavity after IC were calculated and compared between the 2 groups. Treatment toxicities and early survival outcomes were also reported. RESULTS There were no differences in the initial tumor volume and nasopharyngeal cavity between the 2 groups. The volume changes after IC for the primary site, lymph nodes, and nasopharyngeal cavity were 31.4 (range, -0.97-75.8), 4.68 (range, -7.08-22.06), and 2.62 (range, 0.1-7.63) mL for GP and 23.36 (range, -59.14-83.58), 4.7 (range, -11.21-48.61), and 1.47 (range, -2.47-6.17) mL for TP, respectively. All comparisons favored the GP regimen. The toxicities of the 2 regimens were comparable and no survival differences were observed at follow-up (median, 18.7 months). CONCLUSIONS Changes in the tumor volume and nasopharyngeal air cavity showed that the GP regimen was significantly more effective than the TP regimen in tumor burden reduction. However, whether the advantages of GP can translate into survival benefits requires further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction chemotherapy for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Efficacy and safety of the TPC regimen compared to GP and TPF.Oral Oncol. 2025 Jan;160:107119. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2024.107119. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Oral Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39591693
-
Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus docetaxel and cisplatin as induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma from non-endemic area of China.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Sep;146(9):2369-2378. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03229-3. Epub 2020 May 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32363479 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of three induction chemotherapy regimens with gemcitabine plus cisplatin (GP), cisplatin plus fluorouracil (PF) and cisplatin plus capecitabine (PX) for locoregionally advanced previously untreated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A pooled analysis of two prospective studies.Oral Oncol. 2021 Mar;114:105158. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.105158. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Oral Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33508707
-
Induction treatment prior to chemoradiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: triplet or doublet chemotherapy?Anticancer Drugs. 2020 Feb;31(2):97-100. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000867. Anticancer Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31815764 Review.
-
The Most Efficacious Induction Chemotherapy Regimen for Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;11:626145. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626145. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718193 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gemcitabine Plus Platinum versus Docetaxel Plus Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Randomized Clinical Study.Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2021 May-Aug;9(2):125-134. doi: 10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_471_20. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Saudi J Med Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34084103 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor volume reduction after induction chemotherapy with gemcitabine plus cisplatin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 May;280(5):2497-2509. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07809-6. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36572820
-
Optimizing induction chemotherapy regimens for radiotherapy in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2023 Apr;12(8):9449-9457. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5707. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36872566 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and safety of gemcitabine plus cisplatin induction chemotherapy in patients with locoregionally advanced NPC.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 May;279(5):2441-2450. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07033-8. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34410469
-
The change in tumor volume after induction chemotherapy with docetaxel plus cisplatin in 259 nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Aug;278(8):3027-3035. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06477-8. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33386968
References
-
- Zong J, Lin S, Lin J, et al. Impact of intensity-modulated radiotherapy on nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Validation of the 7th edition AJCC staging system. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:254–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

